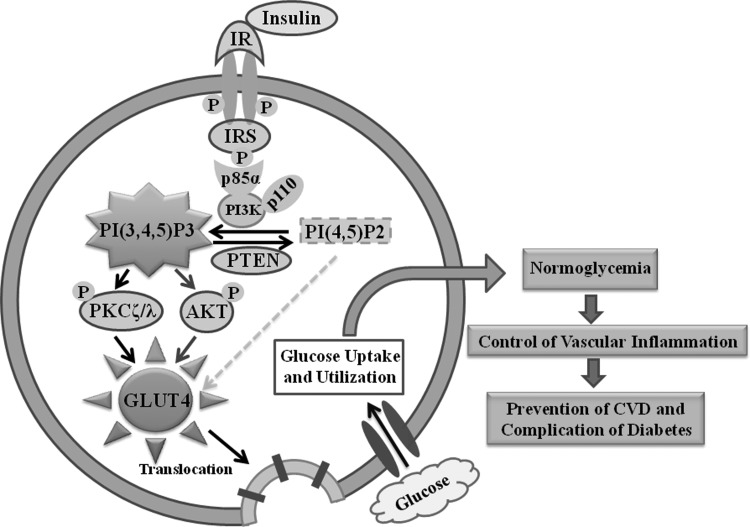
FIG. 2.
Insulin stimulated signaling cascade of glucose metabolism. Binding of insulin with its receptor (IR) undergoes receptor autophosphorylation and enhances its kinase activity. Subsequent binding of IRS (insulin receptor substrate) with the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) upregulates the synthesis of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 utilizing PtdIns(4,5)P2 as a substrate. The phosphatase, PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10) dephosphorylates PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 at the 3′-position. Formation of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 activates downstream effector protein molecules, Akt (serine/threonine protein kinase) and PKCζ/λ (protein kinase C zeta/lambda). This causes the translocation of GLUT (glucose transporter) from intracellular site to the plasma membrane followed by glucose uptake and utilization by the cells leading to normoglycemia, control of vascular inflammation, and prevention of CVD (cardiovascular diseases) and the complications of diabetes.