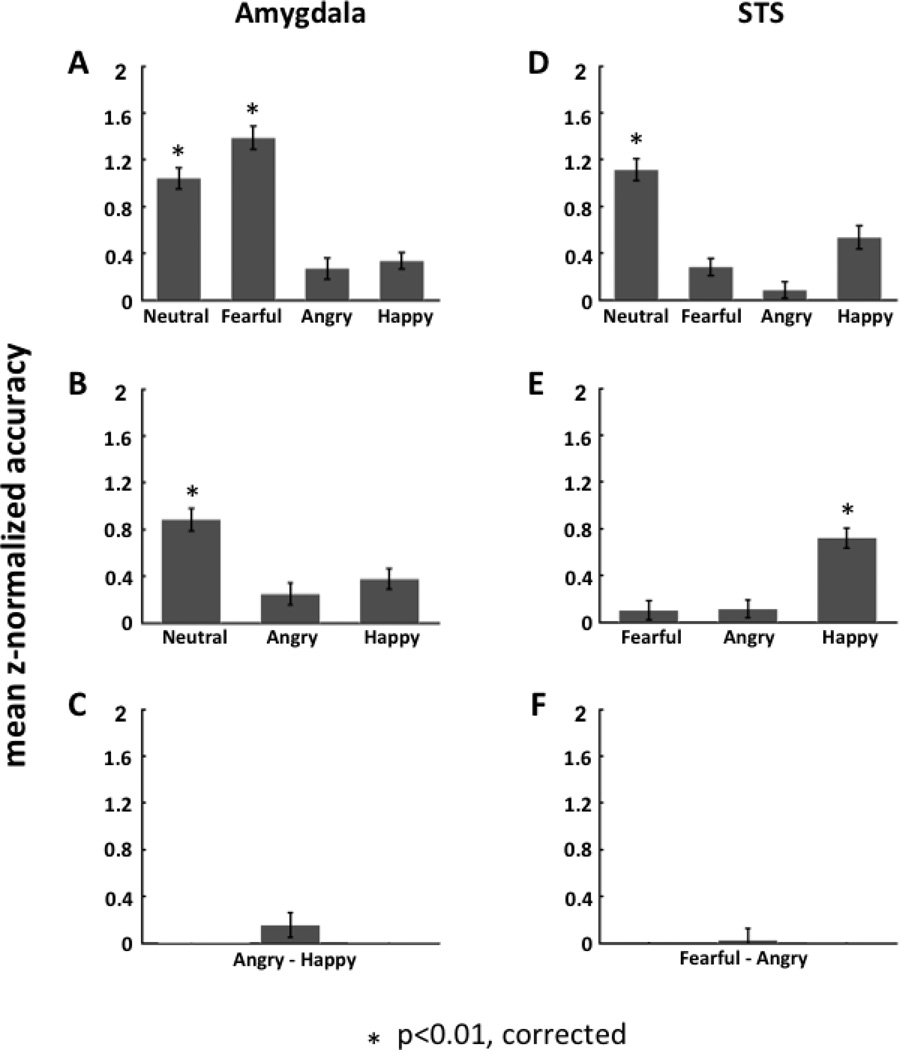
Figure 4.
Hierarchical classification analysis of facial expression in the amygdala and posterior STS. The hierarchical structure was calculated by applying one-versus-all SVM classification at each level of the binary tree architecture. In the amygdala (panels A–C), the classification of fearful and non-fearful faces was at the top of the hierarchy and showed significant accuracy of discrimination between the two (A); the classification of neutral and emotional faces (angry and happy) was at the second level and showed significant accuracy of discrimination (B); the classification of happy and angry faces was at the bottom of the hierarchy but did not show significant accuracy of discrimination (C). In contrast, in STS (panels D–F), the classification of neutral and emotional faces (fearful, angry and happy) was at the top of the hierarchy and showed significant accuracy of discrimination (D); the classification of positive (happy) and negative (fearful and angry) expressions was at the second level and showed significant accuracy of discrimination (E); the classification of angry and fearful faces was at the bottom of the hierarchy and did not show significant accuracy of discrimination (F).