Figure 9.
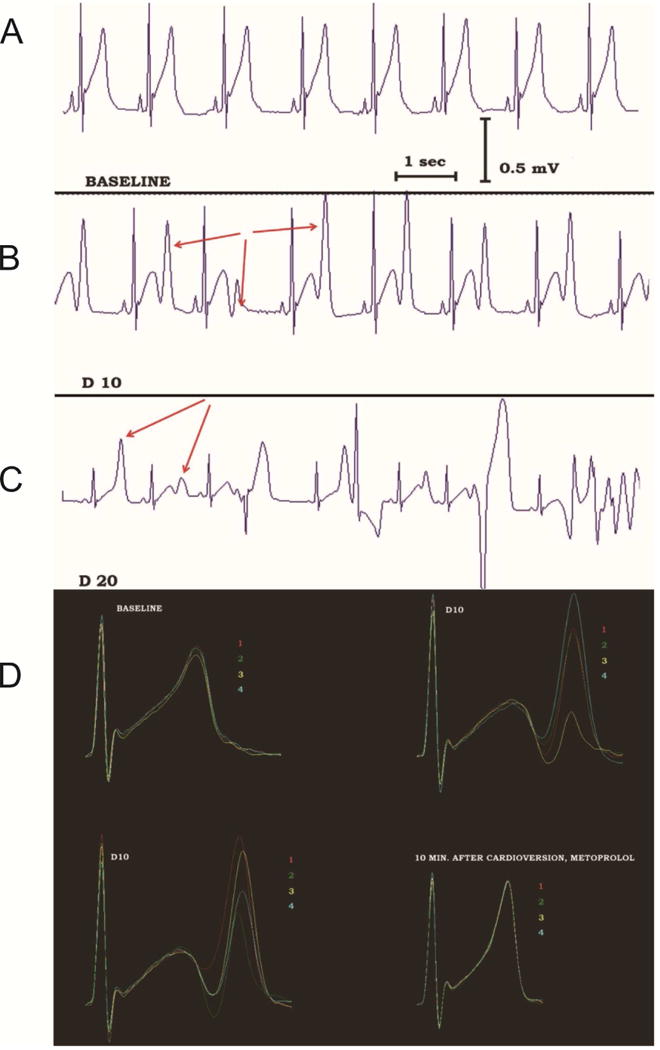
Non-alternans repolarization lability precedes TdP onset in a patient with congenital LQTS during dobutamine infusion. A: Before dobutamine infusion, sinus rhythm without obvious repolarization lability is recorded. B: During dobutamine infusion (dose of 10 μg/kg/minute), sinus rhythm is still present without ectopic beats, but the terminal component of the T-wave fluctuates dramatically in amplitude (red arrows) without an alternans pattern. C: With increased dobutamine dose (20 μg/kg/minute), TdP develops, preceded by polymorphic ventricular ectopy. D: The repolarization lability can be easily appreciated when 4 consecutive sinus beats are superimposed and color-coded. At baseline (top left), the repolarization lability is minimal. Striking T wave lability is evident during dobutamine infusion (top right and bottom left). This disappears after electrical cardioversion of TdP, cessation of dobutamine infusion and β-blocker administration (bottom right). Similar repolarization lability is observed in the rabbit LQTS model, when rises along with lability of Cai and Vm signals (not shown). Adapted from67
