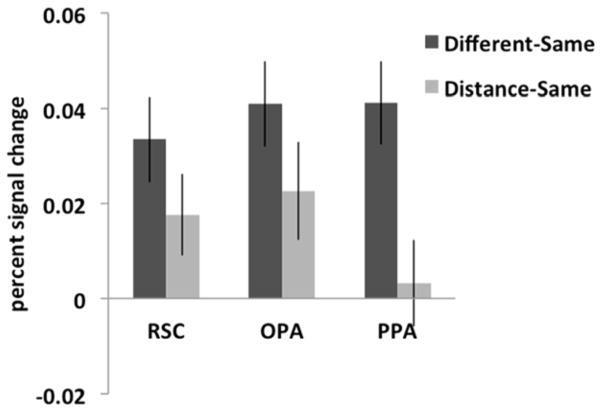
Figure 4.
For each scene-selective ROI, the difference between the peak responses for two different images of scenes and the same images (labeled “Different-Same”) was compared to the difference between the peak responses for two images of the same scene viewed from either a proximal or distal perspective and the opposite version of the same image and the same images (labeled “Distance-Same”). A 3 (ROI: RSC, OPA, PPA) x 2 (difference score: Different-Same, Distance-Same) repeated-measures ANOVA revealed a significant interaction (F(2,50) = 4.35, p < 0.02, ηP2 = 0.15), with a significantly greater difference between the Different and Same conditions than between the Distance and Same conditions for PPA, relative to RSC or OPA. This result suggests that the scene-selective regions represent egocentric distance information differently: RSC and OPA are sensitive to egocentric distance information in scenes, while PPA is not sensitive to such information.