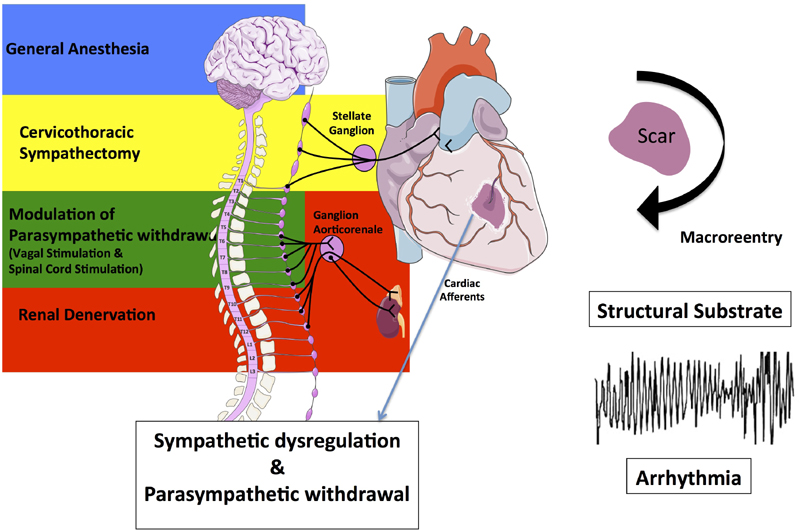
Figure 3.
Impact of ventricular injury on scar generation and subsequent development of a structural substrate for macroreentries and ventricular arrhythmias as well as on cardiac afferents resulting in sympathetic dysregulation and parasympathetic withdrawal. Different regulatory centers of cardiac efferent sympathetic (brain, stellate ganglion, renal sympathetic nerves) and parasympathetic (vagus nerve, spinal cord) activation are shown on the left. Interventional strategies to reduce sympathetic activation (e.g. by cardiac sympathetic denervation or renal denervation) or to increase the cardiac parasympathetic tone (e.g. by vagal stimulation and baroreceptor stimulation) are provided.