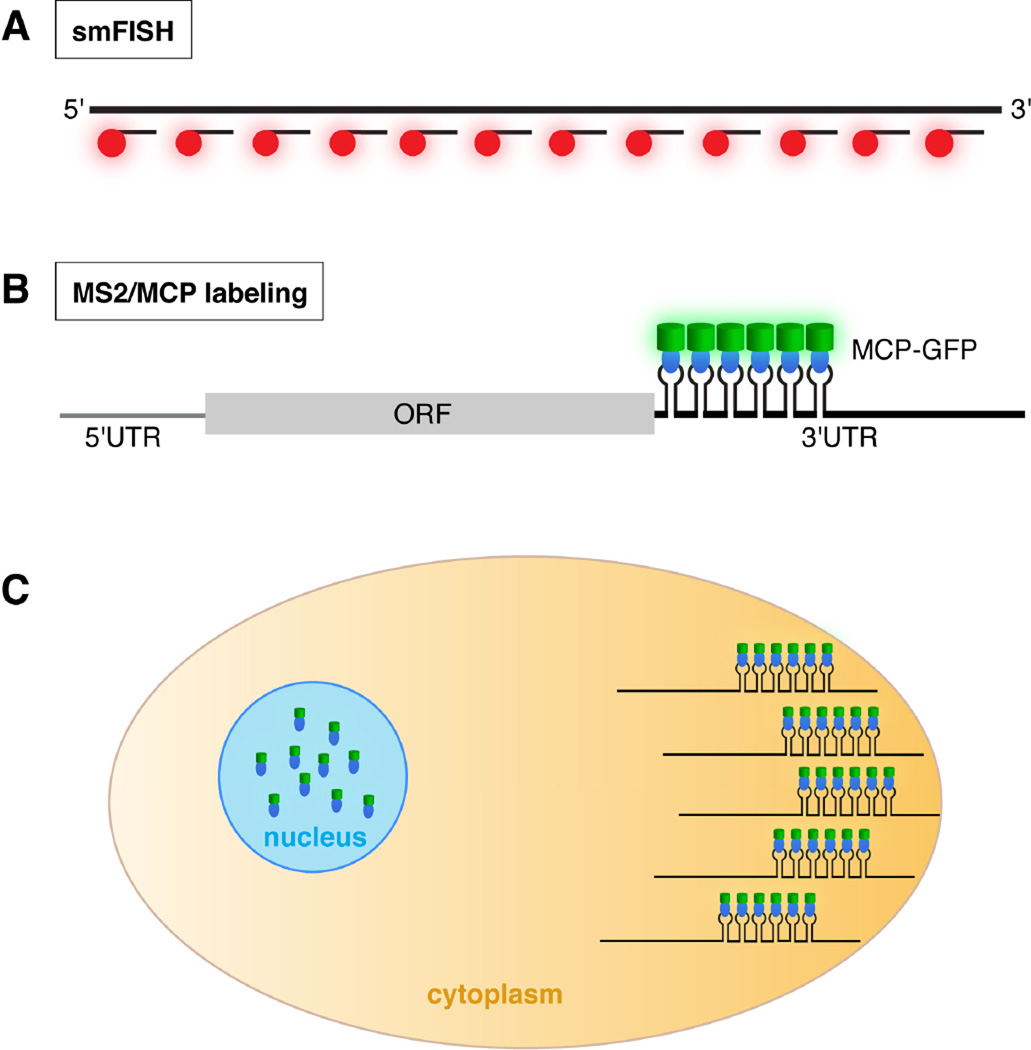
Fig. 1.
Detection of RNA by smFISH and the MS2/MCP labeling system. A. In smFISH, many short probes, each coupled to a fluorophore (red), hybridize along the length of the target RNA (at top). The large number of fluors decorating each RNA molecule results in high signal intensity with low background. B. When transcripts engineered with MS2 stem-loops are co-expressed with MCP-GFP (blue oval: MCP; green cylinder: GFP), binding of MCP-GFP to its cognate stem-loops results in fluorescently labeled mRNA. In this example, the MS2 stem-loops are located at the beginning of the 3’ UTR. C. Cartoon of a cell illustrating detection of a localized mRNA labeled using the MS2/MCP system. For mRNA localization studies, the MCP-FP contains a nuclear localization signal. As a result, MCP-FP molecules not bound to MS2-tagged transcripts are sequestered in the nucleus, reducing background fluorescence.