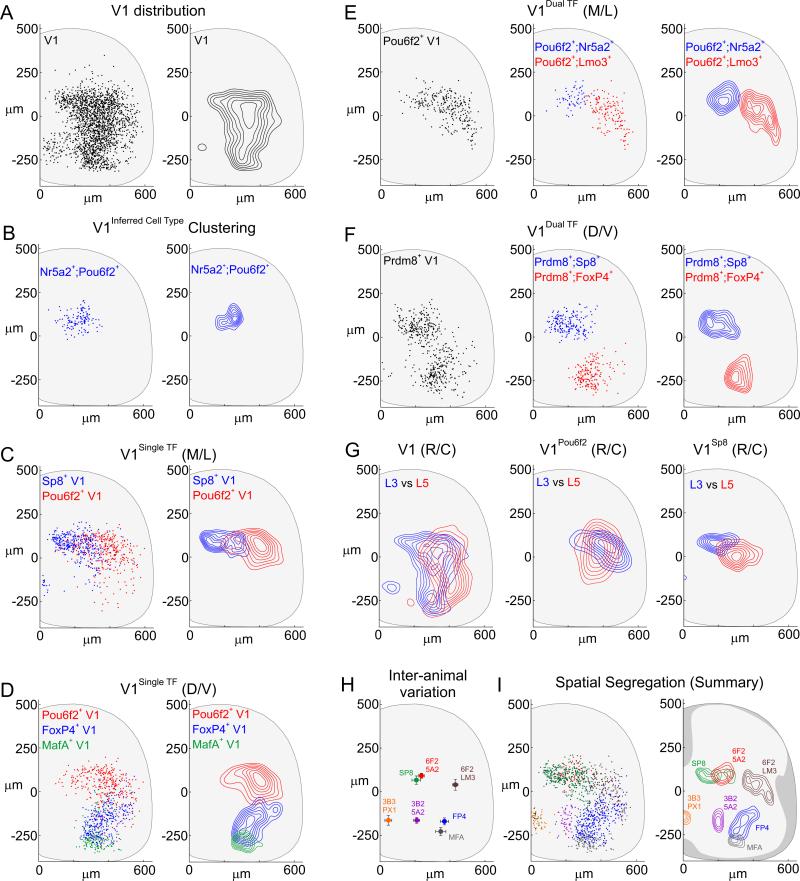
Figure 3. Spatial Segregation of V1 Interneuron Subpopulations.
(A) V1 interneurons in p0 L3-L5 segments of En1.nLacZ mice. D/V axis range: 132 to −265 μm; M/L axis range: 127 to 487 μm, 5th-95th percentiles from central canal. Contours represent density at the 30th-90th percentiles.
(B) Spatial clustering of V1Pou6f2/Nr5a2 interneurons (blue, Fa = 0.236) (p < 0.00001, one-tailed Monte Carlo test compared to parental V1).
(C) M/L biases in distributions of V1Sp8 (Xepicenter = 162 μm) and V1Pou6f2 (Xepi = 403 μm) interneurons. p < 1 × 10−20, Wilcoxon Rank Sum test in x-axis, V1Sp8 or V1Pou6f2 vs V1Parental, and V1Sp8 vs V1Pou6f2.
(D) D/V biases in distributions of V1Pou6f2 (Yepi = 66 μm), V1FoxP4 (Yepi = −158 μm), and V1MafA (Yepi = −277 μm) interneurons. V1Sp8 interneurons (Yepi = 72 μm) also occupy a dorsal position. p < 1 × 10−20, Wilcoxon Rank Sum test in y-axis for V1Pou6f2, V1FoxP4, V1MafA, or V1Sp8 vs V1Parental.
E) Subdivision of V1Pou6f2 interneurons into medial (Nr5a2+, blue) and lateral (Lmo3+, red) subsets in p0 L3-L4 spinal segments.
(F) V1Prdm8 interneurons fractionate into dorsal Sp8+ (blue) and ventral FoxP4+ (red) composite groups.
(G) V1, V1Pou6f2, and V1Sp8 settling position at L3 (blue) or L5 (red) in p0 mice. p < 0.0001 for L3 vs L5, 2D KS test.
(H) Constancy of x,y position (mean ± SD) for V1 interneurons expressing Sp8 (n = 7), Pou6f2/Nr5a2 (n = 8), Pou6f2/Lmo3 (n = 4), FoxP4 (n = 7), Nr3b2/Nr5a2 (n = 8), Nr3b3/Prox1 (n = 6), and MafA (n = 7 animals).
(I) Spatial distributions of seven V1 subsets. Contours represent 60th-90th percentile densities. See also Figures S3 and S4, and Table S1.