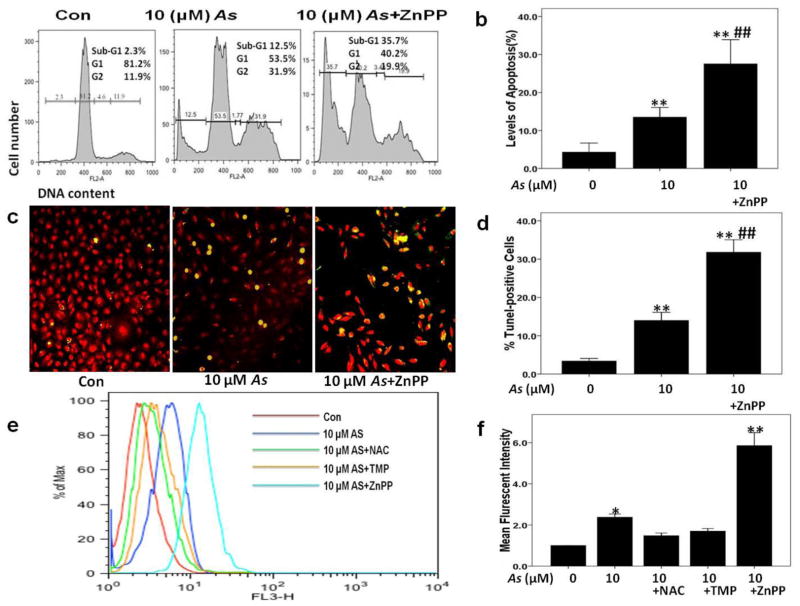
Fig. 2. Blocking HO-1 activity with ZnPP augmented arsenic-induced apoptosis and ROS production.
Apoptosis levels and intracellular ROS production were measured 24 h after arsenic (As) treatment with or without 2 μM ZnPP pretreatment of HK-2 cells. (a–b) Levels of apoptosis were calculated by evaluating the percentage of cells accumulated in the sub-G1 position after PI staining DNA. (c–d) Apoptosis was determined by TUNEL staining, and average percentages of TUNLE-positive cells were assessed in each group. (e–f) 100 μM TMP and 10 mM NAC inhibited As-induced ROS generation at 24 h, while 2 μM ZnPP augmented ROS generation. Values are mean ± SD (n=3), (*) p<0.05 vs Con; (**) p<0.01 vs Con; (##) p<0.01 vs. 10μM As.