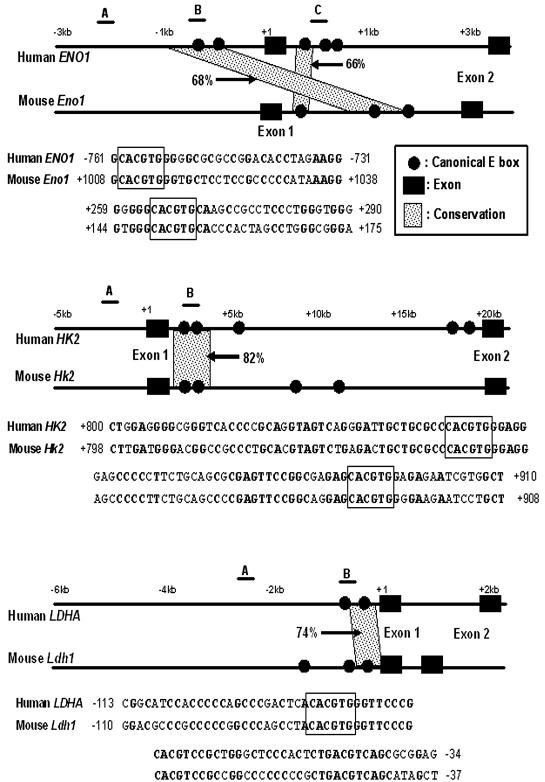
FIG. 1.
Locations of canonical E boxes in the human and mouse genomic sequences and phylogenetic footprinting analysis. Genomic sequences containing 5 kb upstream of the transcriptional start site through intron 1 were screened for the presence of the canonical E box. The positions of canonical E boxes and exons are mapped in the human (top of each pair) and mouse (bottom of each pair) genomic sequences. The maps show phylogenetically conserved canonical E boxes in ENO1, HK2, and LDHA genes. Conserved canonical E boxes were identified using the dot plot features of OMIGA software. Conservation of the canonical E box and its extended flanking region with more than 65% sequence identity for longer than 30 bp is indicated. The percentages of sequence identity between the two sequences are also indicated in the maps. Sequence alignments of the conserved E box and its extended flanking regions are shown below the maps. Canonical E boxes are boxed in each sequence alignment. Conserved nucleotides are shown in bold type. The regions that are amplified for the ChIP assay are indicated by the lines above the human gene and labeled A, B, or C in the maps.