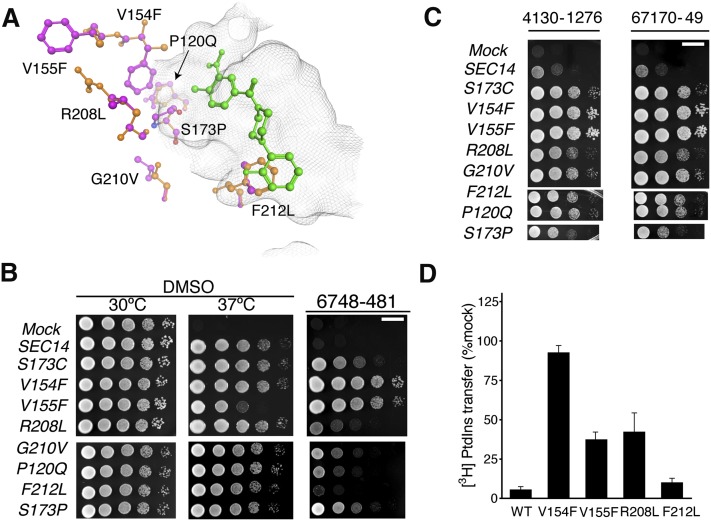
Fig. 3.
Functional characterization of NPPM-resistant Sec14 proteins. A: The seven independently isolated Sec14 missense substitutions identified in NPPMR isolates are highlighted in ball and stick representation with mutant residues depicted in magenta and the corresponding wild-type residues in orange. The positions of the corresponding side chains are related to the NPPM 6748-481 pose depicted in green ball and stick. The surface of the Sec14 hydrophobic pocket is rendered as a gray wire-mesh. B: The indicated SEC14 genes were integrated into the LEU2 locus of a sec14-1ts strain and expressed under the control of the S. cerevisiae SEC14 promoter to generate strains exhibiting “physiological” levels of each Sec14 variant. The integrants were subsequently dilution spotted onto YPD plates supplemented with vehicle control DMSO or 20 μM NPPM, as indicated at top, and incubated for 48 h at the indicated temperatures. The mock condition documents the phenotype of an isogenic strain where a SEC14-less integration cassette was transplaced into the LEU2 locus. That expression of each Sec14 protein was sufficient to rescue sec14-1ts growth defects at the restrictive temperature of 37°C is demonstrated by comparison of the growth profiles in the left (30°C) and center (37°C) panels of the integrants relative to mock controls. The NPPMR phenotypes are displayed in the right panel. The plates were incubated for 48 h at the indicated temperatures before imaging. The NPPM481-resistance phenotypes were scored at 30°C. Note that R208L and F212L were weak mutants. Scale bar, 1 cm. C: Indicates that spontaneous mutants generated in response to 6748-481 confer pan-NPPM resistance to Sec14. The experiment is the same as above in (B) except that the plates were supplemented with NPPMs 4130-1276 and 67170-49, as indicated (20 μM final concentration). The mock condition documents the phenotype of an isogenic strain where a SEC14-less integration cassette was transplaced into the LEU2 locus. Scale bar, 1 cm. (D) NPPMR Sec14 proteins were expressed and purified as recombinant proteins and [3H]PtdIns transfer activities were measured in vitro in the presence of 20 μM NPPM. Protein concentration was clamped at 287 nM. Inhibition was normalized to the DMSO vehicle control. Values are representative of mean ± SEM; triplicate measurements from three independent experiments. The intrinsic PtdIns-transfer activities measured for each Sec14R and other assay statistics are provided in supplementary Table 5.