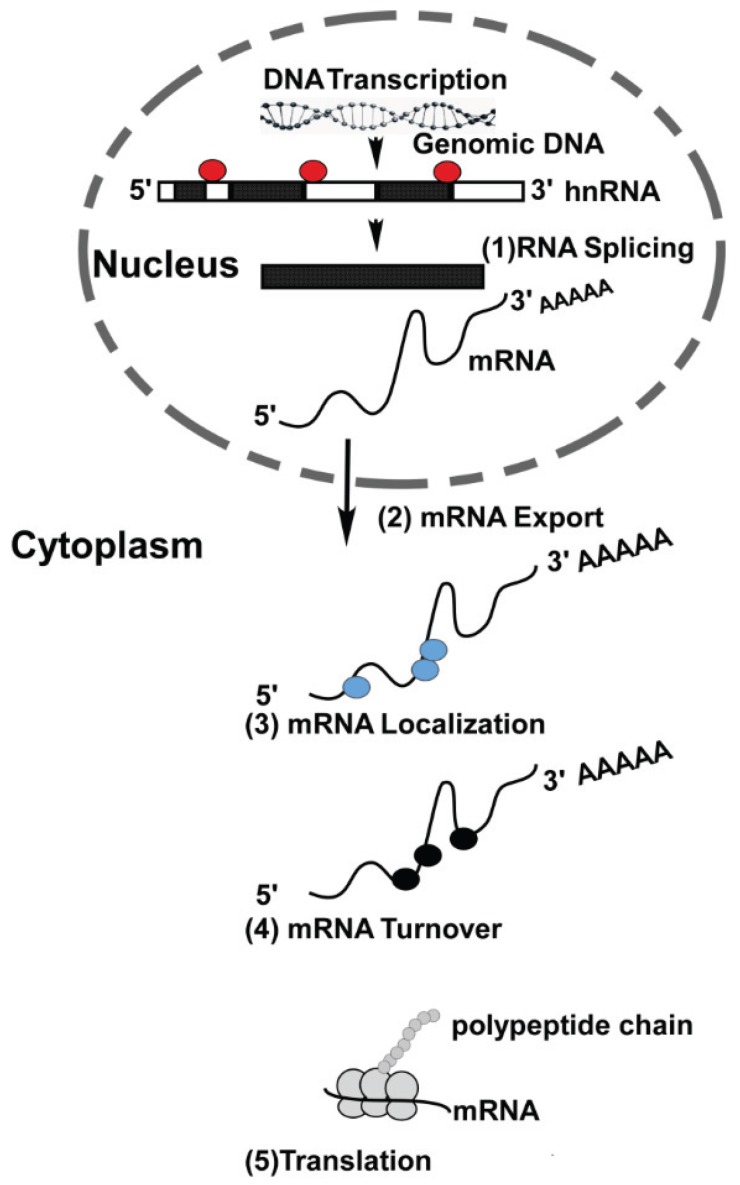
Figure 1.
RNA-binding proteins and their role in RNA metabolism: Genomic DNA is transcribed in the nucleus resulting in generation of hnRNA. RNA-binding proteins (RBP) are involved in (1) splicing and alternative splicing of hnRNA, resulting in the formation of mRNAs. Messenger RNAs are then transported from nucleus into the cytoplasm (2). In the cytoplasm, RBPs aid in the localization of mRNAs to their final destination site (3). Once in the cytoplasm, each mRNA has a specific turn-over rate (4) that can be modulated by association with selective RBPs. The turn-over rate of mRNAs in cells can be altered in response to intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli. Messenger RNAs serve as a template for translation and RBPs play an important role in translation (5).