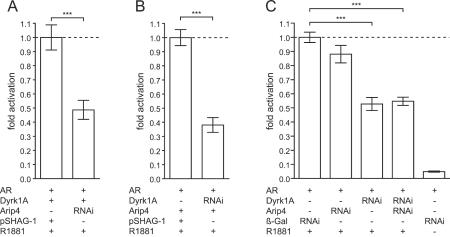
FIG. 7.
Effect of Dyrk1A and Arip4 knockdown by RNAi on AR-dependent transactivation. (A) Endogenous Arip4 is necessary for the full effect of Dyrk1A on AR-mediated transcription. Dyrk1A was ectopically expressed, and Arip4 expression was either unaltered (−) or inhibited by RNAi. RNAi targeting of Arip4 strongly reduced the effect of Dyrk1A. Values are expressed relative to that obtained by expression of Dyrk1A without knockdown of Arip4 (with pSHAG-1 as a control; value set at 1; left bar). (B) Endogenous Dyrk1A is necessary for the full effect of Arip4 on AR-mediated transcription. Arip4 was ectopically expressed, and Dyrk1A expression was either unaltered (−) or inhibited by RNAi. RNAi targeting of Dyrk1A strongly reduced the effect of Arip4. Values are expressed relative to that obtained by expression of Arip4 without knockdown of Dyrk1A (with pSHAG-1 as a control; value set at 1; left bar). (C) Endogenous Dyrk1A and Arip4 both contribute to AR-mediated transactivation. Knockdown of either Dyrk1A (third bar from left) or both Dyrk1A and Arip4 (fourth bar from left) significantly reduced the effect of the synthetic AR agonist R1881 on transcription, compared to the effect seen in controls expressing shRNA specific for the mRNA encoded by the lacZ gene (first bar from left). Values are expressed relative to those for the control (AR and lacZ RNAi in the presence of R1881; values set at 1; first bar from left). Luciferase activities were normalized to protein contents of the lysates. Means and SEMs for three independent experiments are shown. For comparisons indicated by brackets, three asterisks indicate a P value of <0.0001.