Figure 3.
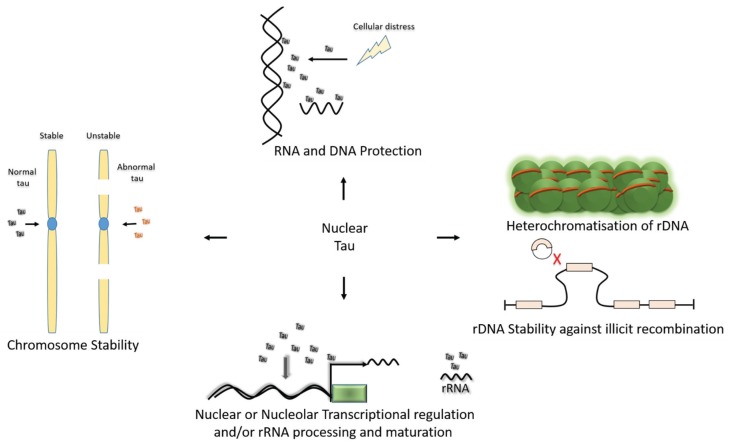
Potential functions of Nuclear tau. Tau has been shown to protect the DNA and RNA from cellular distress [52,53]. It has been localised within the nucleolus, at the vicinity of the rDNA and associated with a markers of the heterochromatin, within the nucleolus, it specifically localises to the dense fibrillar component (DFC) of the nucleolus—a region involved with rDNA transcription and processing of nascent pre-rRNA; collectively, this suggests a potential role for tau in either rDNA heterochromatisation and stability, rDNA transcription and/or rRNA processing and maturation [3,57,62]. Data from cell culture and human cells with varying tau mutations also provides strong evidence for tau in the maitenance of chromosomal stability [2,87]. The nature of interaction of tau-DNA interaction also suggests it could be be involved in nuclear transcriptional regulation (See below for more detailed discussion). All these functions need further research to be completely validated.