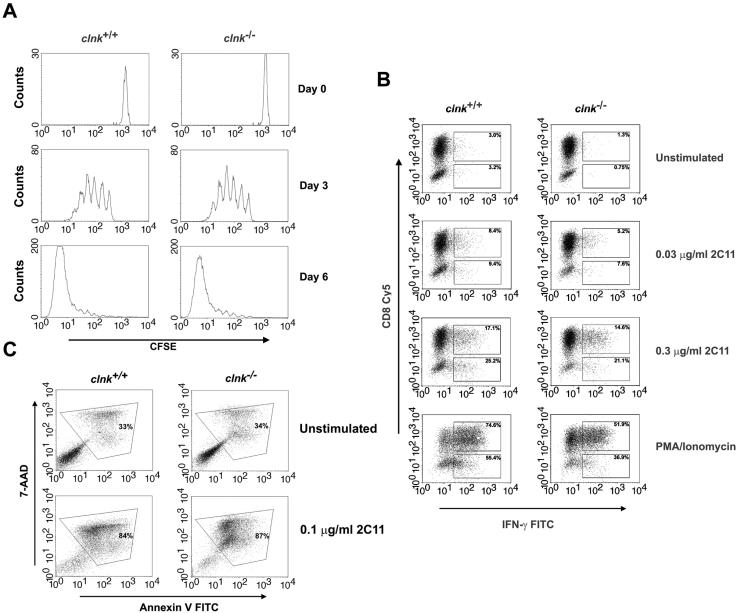
FIG. 2.
In vitro assays of T-cell functions. (A) T-cell proliferation. T cells were labeled with CFSE and stimulated by use of plastic coated with anti-CD3 MAb 145-2C11 (1 μg per ml) in the presence of 100 U of IL-2 per ml. T-cell proliferation was assessed by measuring CFSE labeling at the indicated times after the initial stimulation. Proliferation of T cells causes a progressive loss in CFSE label. (B) TCR-induced production of IFN-γ. T cells were stimulated for 48 h with anti-CD3 MAb 145-2C11 and then expanded for 5 days in IL-2-supplemented growth medium. After being washed, cells were stimulated for 4 h and analyzed for IFN-γ production by intracellular staining with FITC-coupled anti-IFN-γ antibodies. CD8+ T cells were identified by concomitant staining with Cy5-labeled anti-CD8. CD8− T cells presumably represent CD4+ cells. Percentages indicate the proportions of cells (CD8+ or CD8−) showing appreciable IFN-γ secretion. (C) Activation-induced T-cell death. T cells were stimulated for 48 h with anti-CD3 and expanded for 5 days with IL-2. Cells were then stimulated or not with plate-bound anti-CD3 MAb 145-2C11. This type of activation protocol is known to trigger AICD. After 18 h, AICD was assessed by staining cells with 7-AAD and FITC-labeled annexin V. Apoptotic cells (boxed) are positive for both 7-AAD and annexin V.