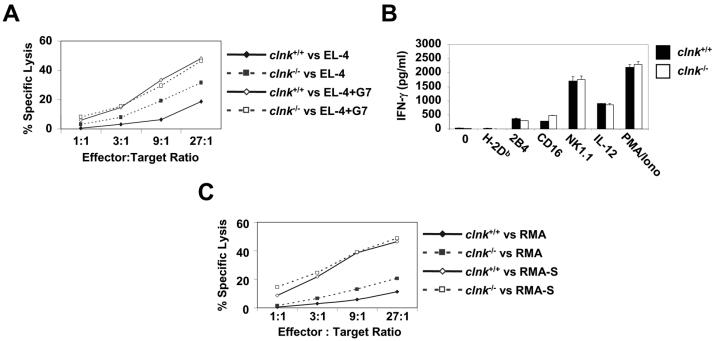
FIG. 5.
Analyses of NK cell functions. (A) Antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. NK cells were incubated at the indicated ratios of effector cells to target cells with 51Cr-labeled EL-4 target cells, in the presence or absence of anti-Thy MAb G7 (which binds Thy1 on EL-4 and triggers CD16 on NK cells). Target cell lysis was determined by measuring 51Cr release in the supernatant (values are percentages of maximal release). Standard deviations are shown. (B) IFN-γ secretion. Cells were stimulated with the indicated antibodies (1 μg per ml), IL-12 (5 ng per ml), or PMA (50 ng per ml) plus ionomycin (1 μg per ml). After 24 h, the production of IFN-γ was measured in the supernatant by ELISA. Standard deviations are shown. Similar results were obtained over a range of different antibody concentrations (data not shown). Standard deviations are represented. (C) Natural cytotoxicity. NK cells were stimulated at the indicated ratios of effector cells to target cells with 51Cr-labeled RMA (MHC class I-positive) or RMA-S (MHC class I-negative) cells. After 4 h, natural killing was assessed by measuring the release of 51Cr in the medium. Values are presented as percentages of maximal release. Standard deviations are shown.