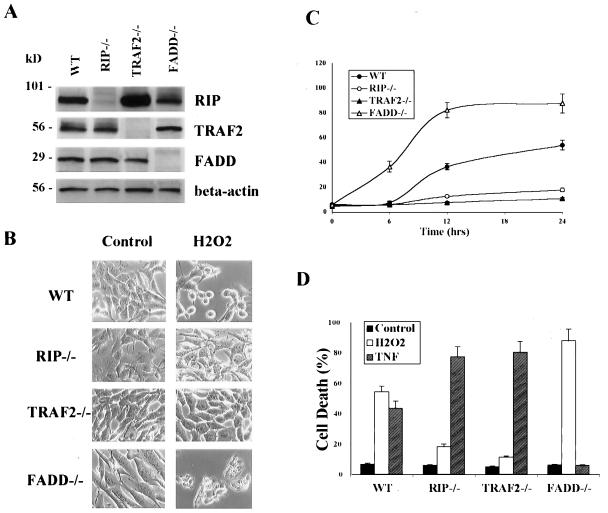
FIG. 1.
Different susceptibilities of RIP−/−, TRAF2−/−, and FADD−/− MEF to H2O2-induced cell death. (A) Western blotting confirmed the absence of RIP, TRAF2, and FADD proteins in their respective knockout cells. (B) H2O2-induced cell death examined by cell morphological changes after H2O2 treatment (500 μM, 12 h). Images were taken under a phase-contrast microscope (×200). (C) H2O2-induced cell death quantified by measuring the percentage of LDH leakage using a cytotoxicity test kit (Roche). Cells were treated with H2O2 (500 μM) for up to 24 h. (D) Opposite pattern of responses towards TNF-α-induced cell death from H2O2. RIP−/− and TRAF2−/− cells were highly sensitive and FADD−/− cells were completely resistant to TNF-induced cell death. Cells were treated with H2O2 (500 μM) or TNF-α (25 ng/ml plus CHX at 10 μg/ml) for 24 h. In both panels C and D, data are presented as means ± standard deviations from at least three independent experiments.