Figure 1. Environmental setting and EEG sources.
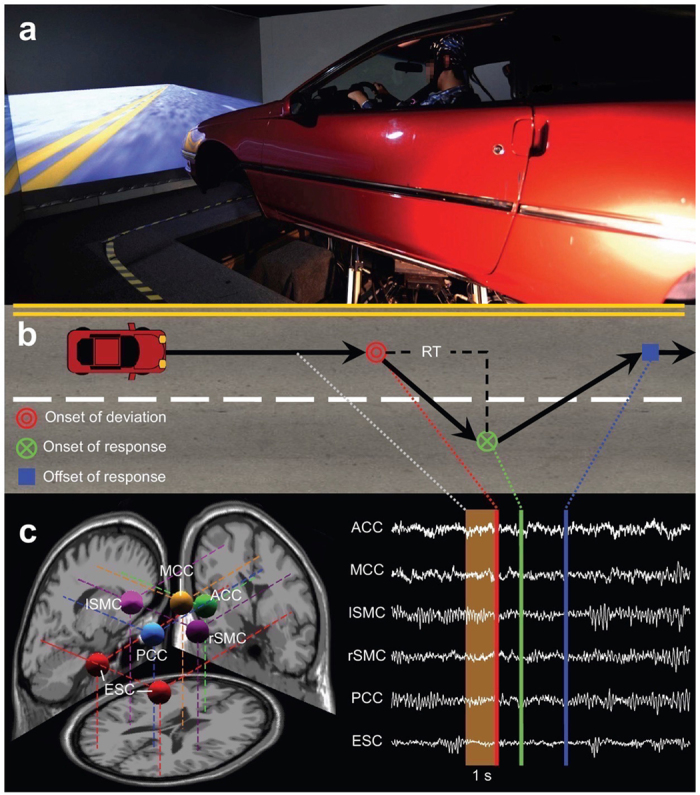
(a) A participant driving the simulated vehicle while EEG is recorded. A six-degree-of-freedom Stewart platform underneath the floor supports the simulator and modulates the orientation of the vehicle to provide the sensation of external motion. (b) Simultaneous behavioral and EEG data were collected throughout the experiment, in which the event-related lane-departure driving paradigm was implemented. Each trial involved three essential events − onset of deviation, onset of response, and offset of response − which were recorded in chronological order. (c) The selected six regions of interest (left panel) and sample time courses of activation (right panel). Effective connectivity measures were derived from independent EEG activations 1-s before onset of perturbations to compute causal relationship between brain regions.
