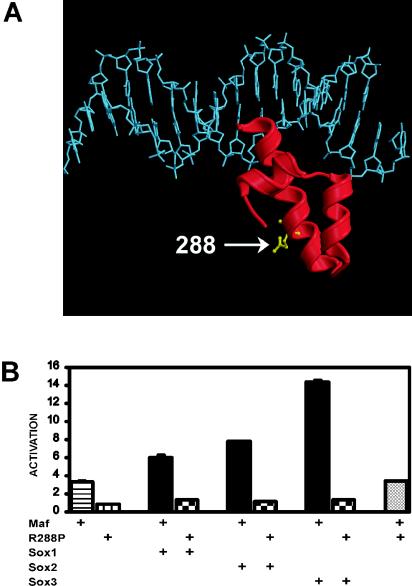
FIG. 3.
R288P mutation in Maf that causes cataracts in humans eliminates transcription activation by Maf alone and together with Sox proteins. (A) Position of the R288P mutation within the ancillary DNA binding domain of Maf. The model shows the structure of the ancillary DNA binding domain of MafG (29) superimposed on the structure of DNA from the Skn-1-DNA complex (44). The residue corresponding to R288 is shown in ball-and-stick representation. The alignment of the ancillary DNA binding domain of Maf is likely to be different from that observed for Skn-1 (8). (B) The R288P mutation in Maf eliminates transcription activation. The efficiencies of transcription activation by the proteins indicated below the bars were measured as described for Fig. 1A. The data represent averages from two independent experiments, each with triplicate samples.