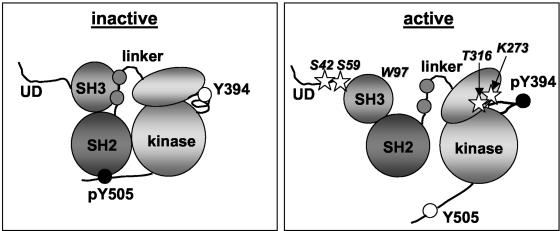
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of inactive and active Lck. The diagram of inactive Lck is based on crystal structures of inactive Src and Hck (43, 53), and the diagram of active Lck is based on the crystal structure of Lck in the autophosphorylated form (56). No structural information is available on the unique domain (UD). Lck undergoes the following major changes upon activation: (i) the inhibitory interactions between the SH2 domain and the regulatory tail and that between the SH3 domain and the linker are released, (ii) tyrosine 505 in the tail is dephosphorylated and tyrosine 394 in the activation loop is phosphorylated, and (iii) the small lobe of the kinase domain rotates relative to the large lobe. The Lck residues that have been mutated in this study are indicated in the active protein by stars.