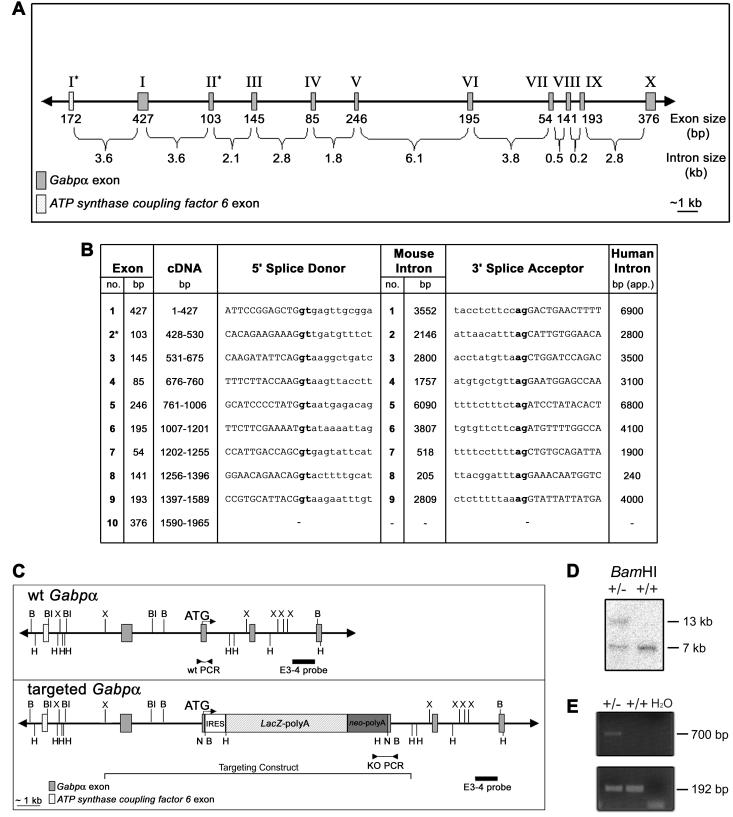
FIG. 1.
Genomic structure and targeted disruption of mouse Gabpα. (A) Schematic of mouse Gabpα genomic structure. Asterisks indicate the first coding exons of Gabpα and the closely linked gene ATP synthase coupling factor 6. (B) Intron-exon boundary sequences of Gabpα and comparison of human (12) and mouse intron sizes. Coding sequences are capitalized, introns are lowercased, and the first coding exon is indicated by an asterisk. Splice sites (gt-ag) are boldfaced. (C) Wild-type (wt) and targeted mouse Gabpα alleles. An IRES-LacZ-neomycin cassette was inserted into exon 2, immediately downstream of the start codon, and the position of the targeting construct (from the XbaI to the HindIII site) is indicated. The positions of the intron-3 probe (external to the targeting construct) used for Southern blot analysis (E3-4) and of PCR primers are indicated. Restriction endonuclease sites are as follows: B, BamHI; Bl, BalI; H, HindIII; N, NotI; X, XbaI. (D) Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones by BamHI digestion and hybridization with the E3-4 probe detecting 7-kb wild-type and 13-kb targeted alleles. (E) PCR screen of wild-type (+/+) and heterozygous (+/−) genomic DNA performed using a 5′ primer within intron 1 (F3) or the neomycin cassette (F8) and a common 3′ primer (B3) immediately downstream of exon 2 to generate 192-bp wild-type and 700-bp targeted PCR products.