Figure 3.
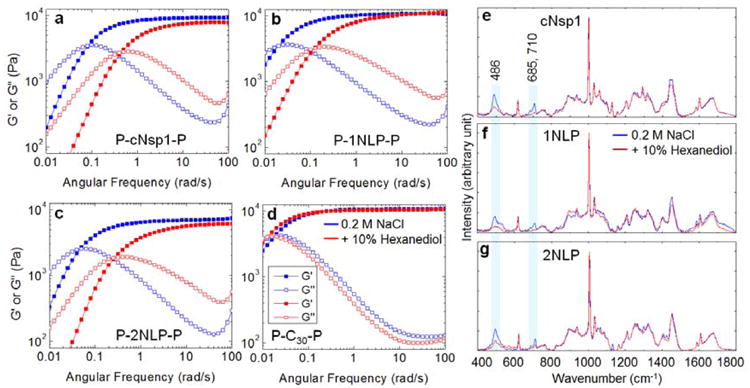
Effect of midblock interactions on hydrogel mechanics. a)-c) Frequency sweep, linear oscillatory shear rheology of 20 w/v% hydrogels in the absence (blue curves) or presence (red curves) of 10 % 1,6 hexanediol. The gel modulus and the crossover frequency in the absence of hexanediol are 9.3 kPa and 0.08 rad/s (a), 10.7 kPa and 0.02 rad/s (b) and 7.5 kPa and 0.04 rad/s (c). Measurements were performed at 25°C with a strain amplitude of 1%, within the linear viscoelastic range (Figure S5). d) Under the same conditions, 20 w/v% P-C30-P gel, which lacks FG repeats in its midblock,27 does not show any effect of the hexanediol (Figure S6). C is the peptide sequence AGAGAGPEG. e)-g) Raman spectra of 20 w/v% midblocks, cNsp1, 1NLP and 2NLP, measured in buffer containing 50 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.5) and 200 mM NaCl (blue curve) and with the addition of 10% hexanediol (red curve). The shaded boxes highlight Raman bands of 486, 685 and 710 cm-1 that decrease in intensity for all protein midblock polymers with the addition of hexanediol. Assignments of other Raman bands for cNsp1 can be found in Figure S7.
