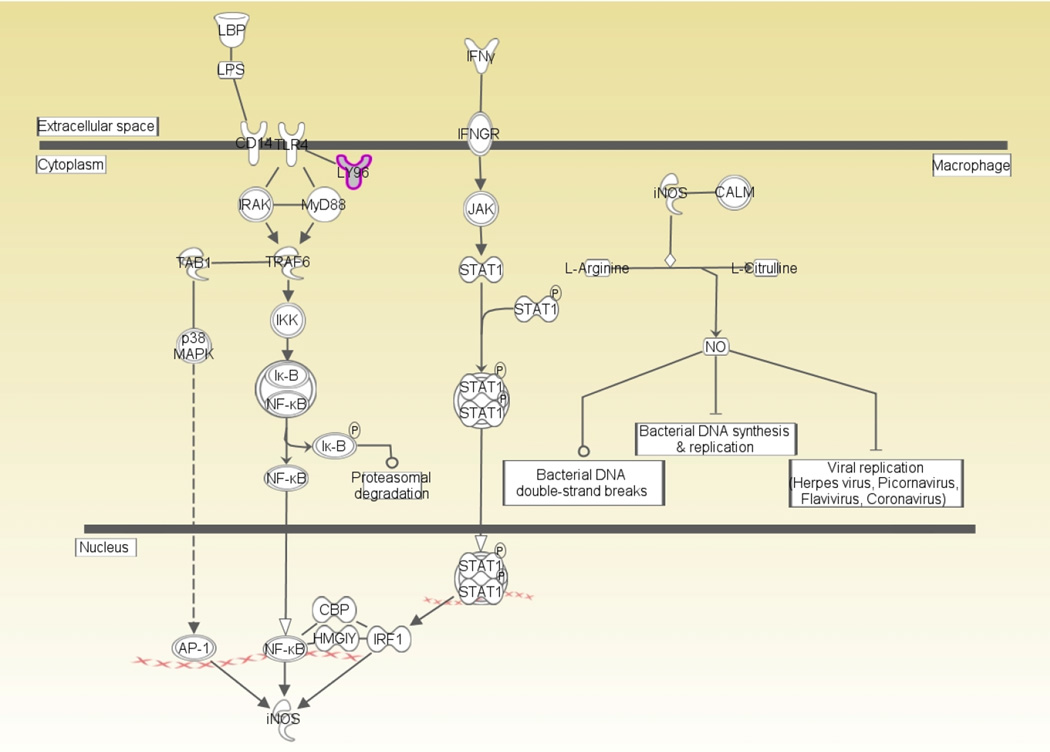
Figure 3. The inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway.
AP-1, activator protein-1; CALM, calmodulin; CBP, cAMP response element-binding protein; CD14, cluster of differentiation; HMGIY, high-mobility group protein; Iκ-B, inhibitor of kappaB protein; IFNγ, interferon gamma; IFNGR, interferon-gamma receptor; IκB-NFκB, inhibitor of kappaB protein-NFkappaB; IKK, inhibitor-of-kappaB-protein kinase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IRAK, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; IRF1, interferon regulatory factor-1; JAK, janus kinase; LBP, lipopolysaccharide binding protein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LY96, lymphocyte antigen 96; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappaB; NO, nitric oxide; p38MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; STAT1 dimer, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 dimer; TAB1, transforming growth factor-beta activated kinase 1; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6.