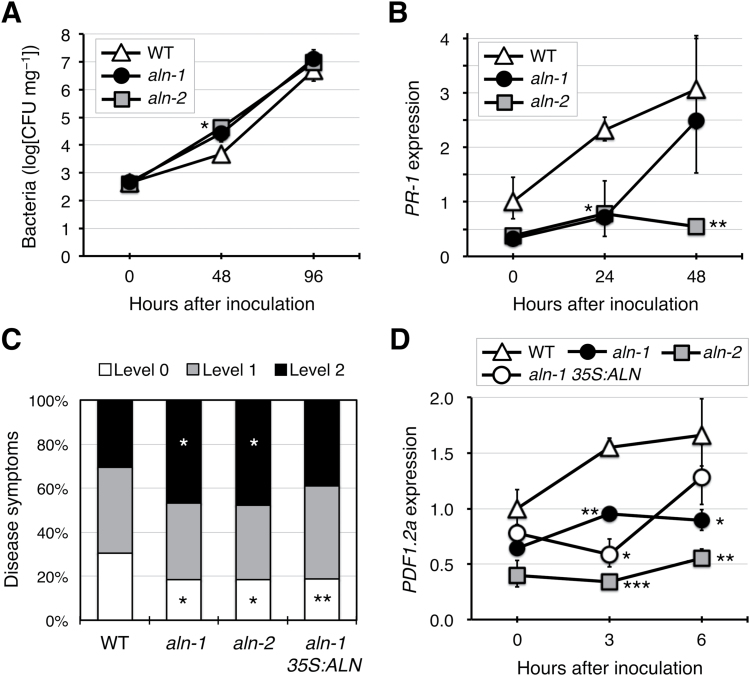
Fig. 4.
Effect of aln mutations on resistance to bacterial pathogens. (A) Resistance to Pst DC3000 was evaluated for 2-week-old seedlings of the WT and two allelic aln mutants (aln-1 and aln-2). At 48 and 96 hpi, internal bacterial populations were determined as mg-1 FW of whole rosettes (n=4). (B) Time-course expression of the SA marker PR-1 in leaves inoculated with Pst DC3000. Relative mRNA levels were determined as described in Fig. 1C and are presented as values relative to those of the WT at zero time. Data are means ±SE from three independent experiments. (C) Resistance to Pcc EC1 was evaluated for leaves from 2-week-old seedlings of the WT, two allelic aln mutants, and the complemented mutant (aln-1 35S:ALN). Disease symptoms were scored at 24 hpi according to three criteria: level 0, no symptoms; level 1, symptoms restricted within the inoculated region; level 2, symptoms extended over the inoculated region (n≥169). (D) Time-course expression of the ERF branch marker PDF1.2a in leaves inoculated with Pcc EC1 was determined as described in (B). Asterisks denote significant differences between WT and mutant plants [*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 by Student’s t-test, except in (C), where Fisher’s exact test was used].