Fig. 5.
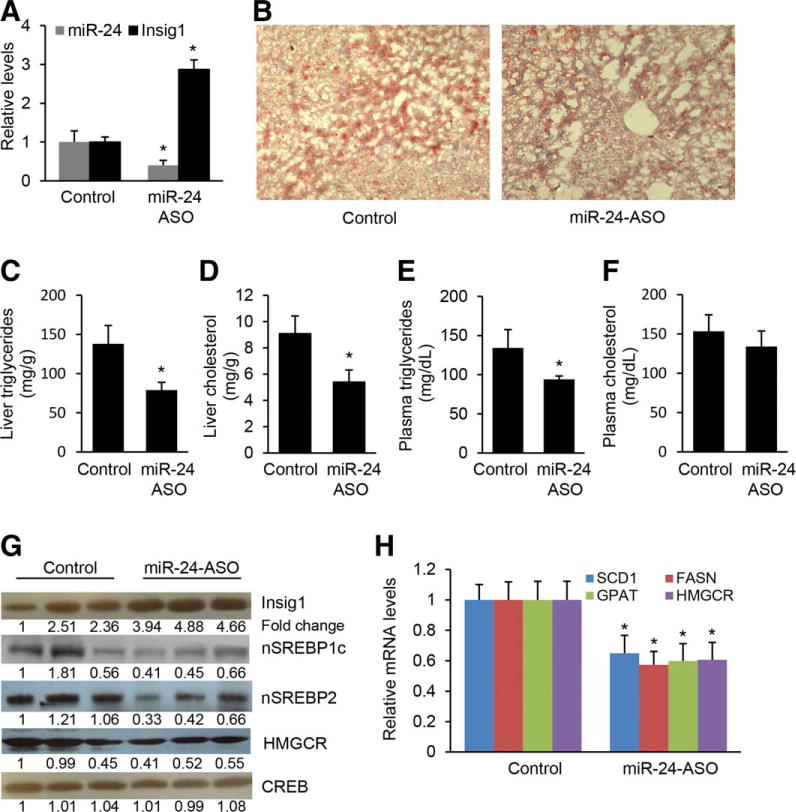
Antagonizing miR-24 prevents hepatic lipid accumulation and hypertriglyceridemia in HFD-treated mice. (A) miR-24-ASO injection resulted in down-regulated miR-24 and increased Insig1 expression in livers of dietary obese mice. (B,C) miR-24 knockdown inhibited lipid accumulation in livers of HFD-fed mice injected with miR-24-ASO as compared to mice injected with miR-24-MM-ASO. Representative images are shown. Cellular triglyceride content was measured by Oil Red staining and triglyceride content (per mg protein) was measured with a triglyceride estimation kit. (D) miR-24 knockdown reduced hepatic cholesterol in HFD-treated mice. (E) Antagonizing miR-24 led to decreased serum triglyceride levels of HFD-fed mice treated with miR-24-ASO (n = 6) as compared to mice injected with miR-24-MM-ASOs (n = 6). (F) miR-24 knockdown had no effect on levels of serum cholesterol. (G) miR-24 knockdown in HFD-treated mice led to an increase in protein levels of Insig1 and prevented nuclear SREBPs processing, which was reflected by decreased nuclear SREBP1c and SREBP2 protein levels in livers of HFD-treated mice with miR-24-ASO injection. Furthermore, HMGCR protein level was decreased due to reduced nuclear SREBP2. (H) qRT-PCR showing that HFD-treated mice with decreased levels of miR-24 also retained reduced expression of SCD1, FASN, GPAT, and HMGCR after miR-24-ASO injection. Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.
