Fig. 6.
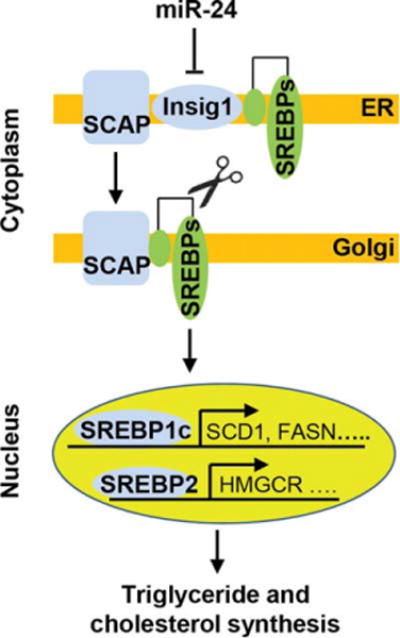
Proposed mechanism by which miR-24 promotes hepatic lipid synthesis. Immature SREBPs form a SREBP-SCAP complex, which is retained in the ER by the interaction between SCAP and the ER-anchoring protein Insig1. By directly inhibiting Insig1 expression, miR-24 facilitates the escape of SCAP-SREBP complex from ER to Golgi, where they are processed by two membrane-bound proteases. The processed SREBP fragments are then released into the cytosol where they then enter the nucleus to activate transcription of lipogenic genes.
