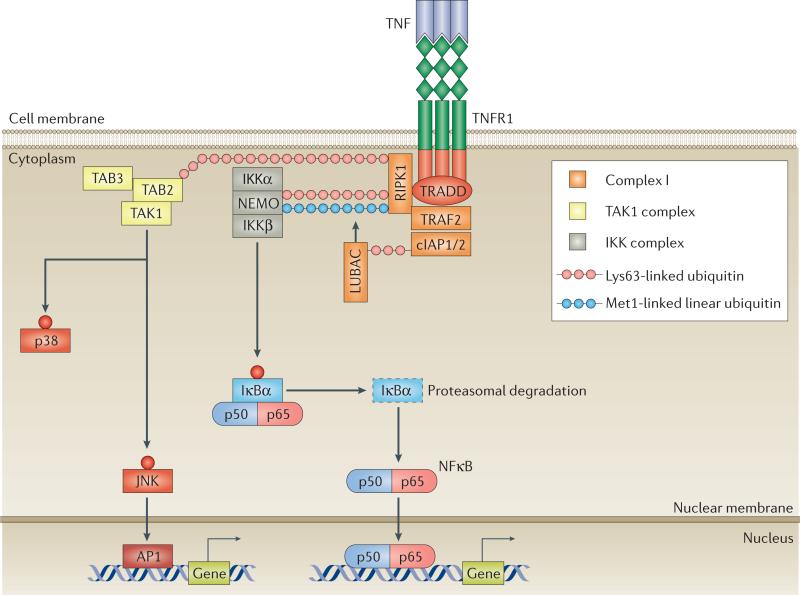
Figure 2. A model of TNFR–complex I signalling.
The binding of homotrimeric TNF to homotrimeric TNF receptors (TNFRs) induces the formation of complex I, comprising TNFR1-associated death domain protein (TRADD), receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), TNFR-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (cIAP1) or cIAP2, and linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC). cIAPs and LUBAC decorate RIPK1 with scaffolding Lys63-linked and Met1-linked polyubiquitin chains, inducing the recruitment of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and inhibitor of κB (IκB) kinase (IKK) complexes. TAK1 activates p38 and JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK), leading to the transcription of AP1-target genes. IKKβ phosphorylates IκB, inducing its proteasomal degradation and the release of nuclear factor κB (NFκB). Free NFκB translocates to the nucleus, where it induces the expression of target genes. NEMO, NFκB essential modulator; TAB, TAK1-binding protein.