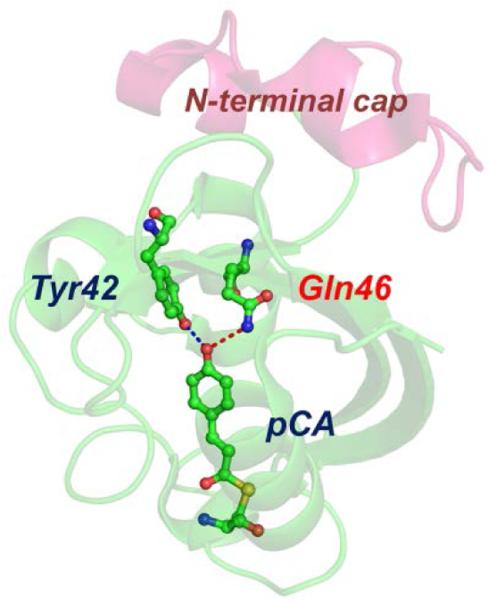
Fig. 1.
Structure of E46Q-PYP. Structures of the protein backbone (ribbon) and the active site around the chromophore (ball-and-stick) in E46Q-PYP (PDB: 1OTA). In E46Q-PYP, the glutamic acid (Glu46) in wild-type PYP was replaced by a glutamine (Gln46). The dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonds between p-coumaric acid (pCA) and the neighbouring residues in the ground state of E46Q. Due to the effect of mutation, the hydrogen bond between pCA and Gln46 is longer than the one between pCA and Glu46 in wild-type PYP.19