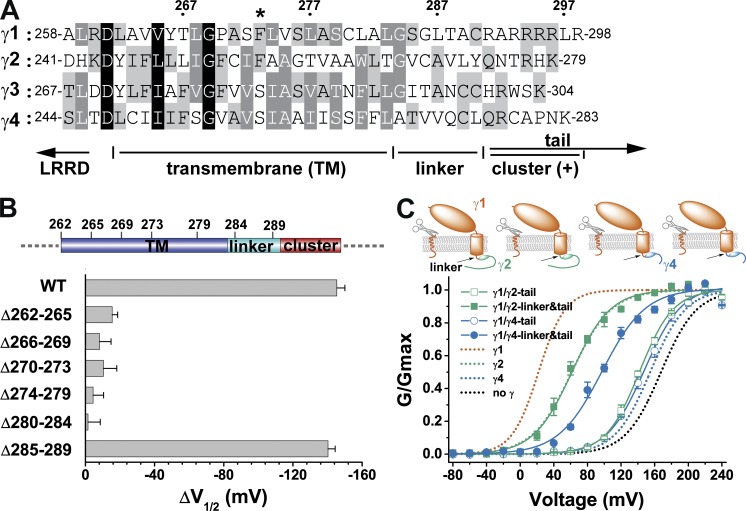
Figure 2.
The presence and function of a linker region. (A) The amino acid sequence alignment of the four BKγ subunits in the region spanning the TM segment and the neighboring cytosolic positively charged cluster. The numbers on top show positions of the corresponding amino acids in the γ1 subunit. The location of the γ1 F273 residue is indicated with an asterisk. Conserved residues are shaded at three levels (from dark to light: 100, 75, and 50%). (B) Shifts in BK channel V1/2 values caused by the wild type and different mutants with deletion of amino acids in the TM and linker regions. The corresponding locations of the deleted amino acids are depicted on top. (C) Voltage dependence of BK channel activation in the presence of different BKγ subunit chimeras, whose main bodies were from γ1 and whose C-tails or C-tails together with linker regions were from γ2 or γ4. For comparison, BK channels expressed by BKα alone or together with wild-type BKγ subunits are shown with dotted lines. Error bars represent ±SEM.