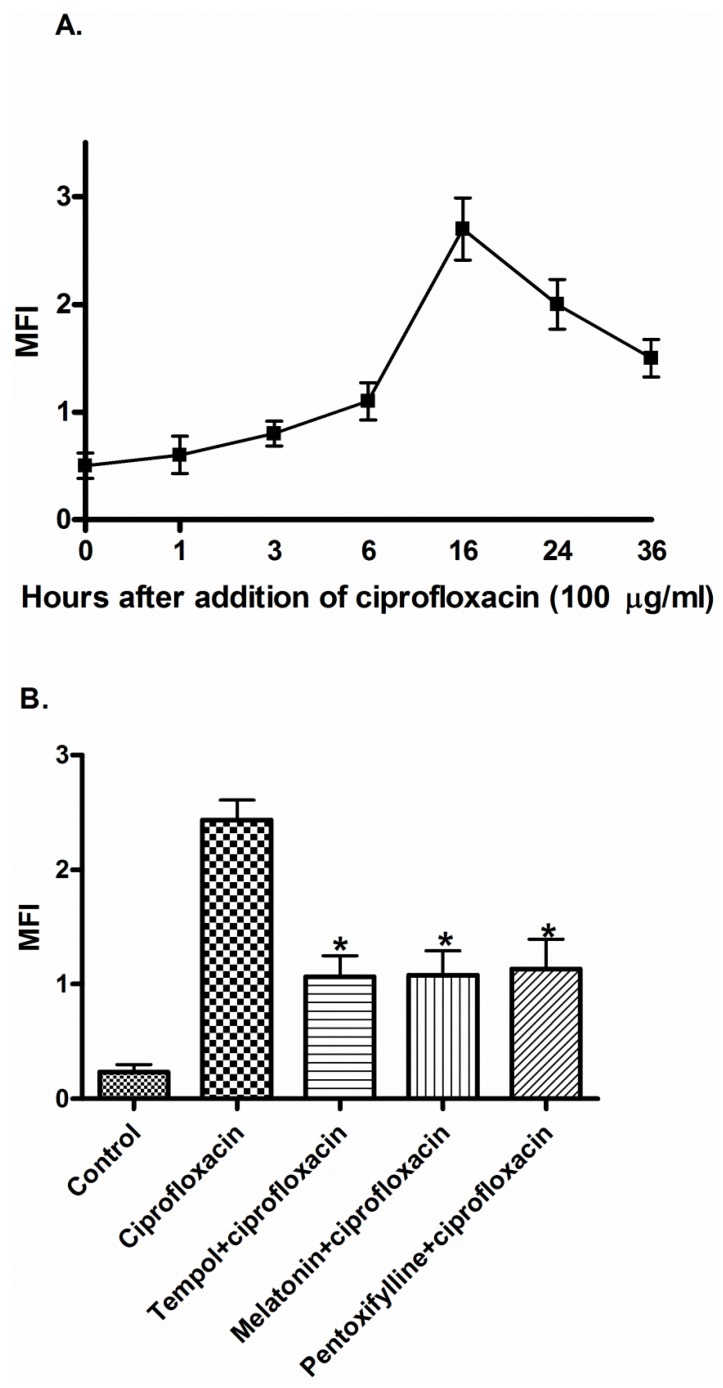
Figure 1.
Ciprofloxacin-induced antibacterial action on E. coli cells is preceded by a time-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Figure 1 (A): Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was shown as the ratio of geometric mean fluorescence intensity of the test sample and the corresponding control. The data shown are representative of three individual experiments. Figure 1 (B): Pretreatment for 16 hour of E. coli cells with tempol, melatonin or pentoxifylline (100 µM) inhibited ciprofloxacin-induced ROS generation. 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA) (10 µM) was added for the last 30 minutes of incubation. The intensity of DCF-DA fluorescence was determined using flowcytometry with an excitation wavelength of 480 nm and an emission wavelength of 530 nm. The data shown are representative of three individual experiments. * indicates significant difference from the control, and ciprofloxacin only treated groups (One way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test, p < 0.05 in each case).