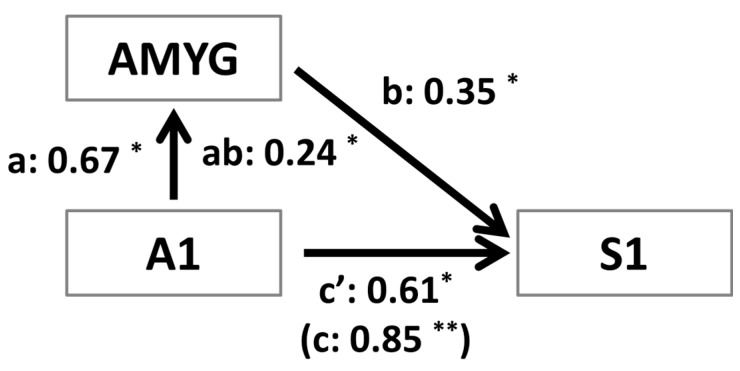
Figure 3.
Mediation analysis at the group-level using the mean responses in each region per participant. For all variables (i.e., regions) in the network, signal differences between CS+ and CS− were used as the dependent measure. Path analysis was used to test the hypothesis that the initial effect of primary auditory reactivity (A1) on the response in the primary sensory cortex (S1) was mediated by reactivity of the amygdala (AMYG). As predicted, we observed a significant mediation effect (i.e., abs = 0.24), and the coefficient of the c’1 path (i.e., the effect of A1 on S1 after controlling for the amygdala as a mediator) was diminished yet still significant. The latter suggests A1 activity had an influence of S1 activity even after controlling for the amygdala mediation. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.