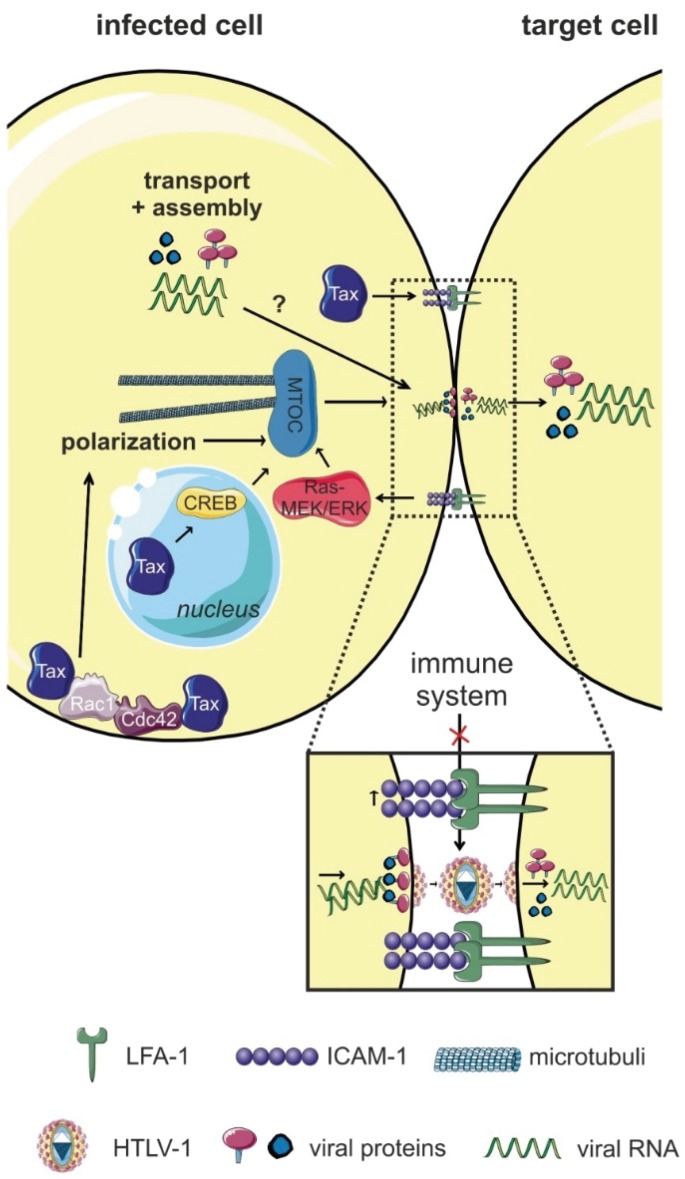
Figure 1.
The virological synapse (VS). Interactions of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1; on HTLV-1-infected T-cells) with lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1; on target cells), and signals induced by the viral Tax protein trigger polarization of the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) towards the cell-cell contact and formation of the VS at the cell-cell contact. Tax is not only located in the nucleus, but also at the MTOC and in the cell-cell contact region. Tax-induced CREB signaling (nuclear activity of Tax), the accumulation of Tax at the MTOC, and ICAM-1-induced Ras/MEK/ERK signaling are important for MTOC polarization. It is assumed that the VS allows for efficient polarized budding and virus transmission via a synaptic cleft, thus, avoiding recognition of HTLV-1 by the host immune system. Figure was realized thanks to Servier Medical Art.