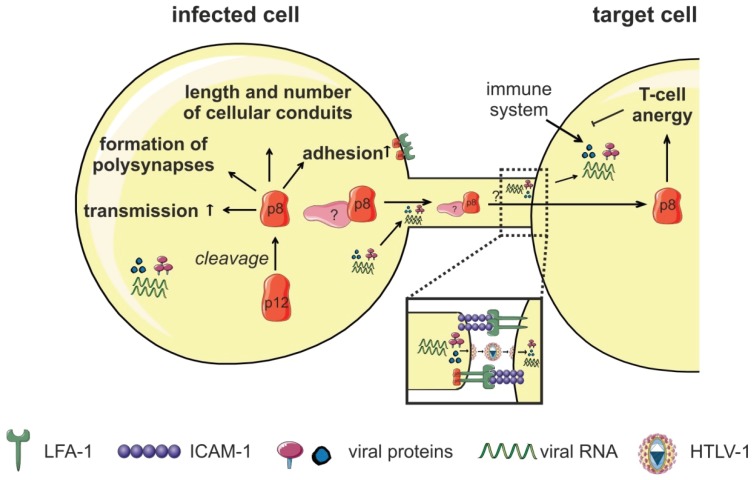
Figure 3.
Cellular conduits. The viral accessory protein p12 is proteolytically cleaved into the p8 protein, which increases adhesion of T-cells through lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) clustering. Further, p8 induces polysynapse formation and enhances the number and length of cellular conduits between T-cells, thereby, enhancing HTLV-1-transmission. p8 is transferred to target cells through these conduits and it is hypothesized to induce T-cell anergy in the target cell. This might be a strategy for HTLV-1 to evade the host’s immune surveillance during infection. Host cell proteins that interact with p8 to enhance conduit formation, p8 transfer, and HTLV-1 transmission are still unknown. Figure was realized thanks to Servier Medical Art.