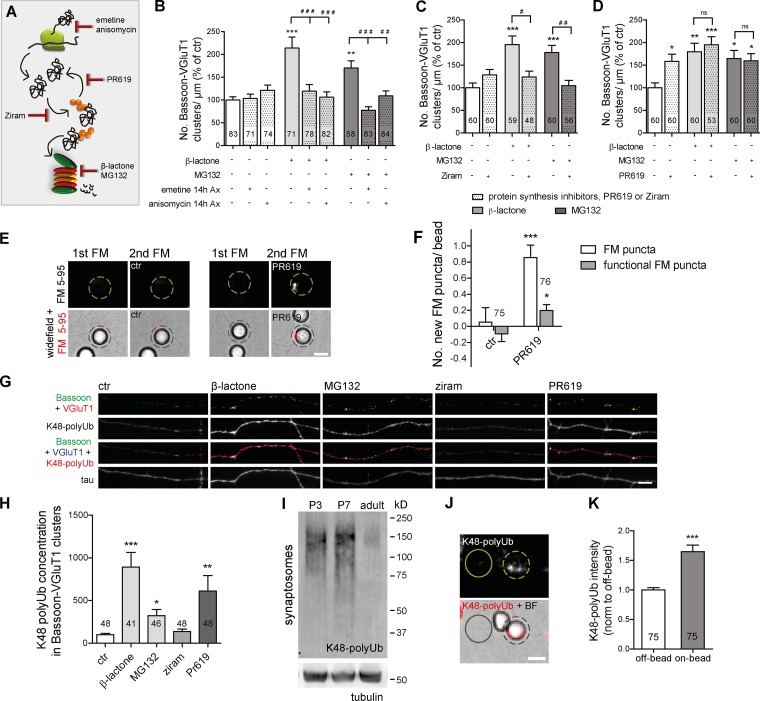
Figure 4.
Presynaptic accumulation of ubiquitinated conjugates is required and sufficient to induce presynaptic assembly. (A) Selective targeting of UPS and protein synthesis. (B–D) Density of presynaptic clusters (percentage of control) after axonal proteasome inhibition in the absence or presence of protein synthesis inhibitors emetine (10 µM) or anisomycin (10 µM; B), ziram (1 µM; C), or PR619 (1 µM; D). Long-term (14 h) inhibition of axonal protein synthesis (B) and inhibition of E1-mediated ubiquitination (1 h; C) abolished the synaptogenic effect of proteasome inhibition. (D) PR619 locally boosted formation of clusters. Five independent experiments. ns, not significant. (E) PR619 led to an increase in the formation of FM puncta on beads (dashed circles; protocol; Fig. 1, D and E). (F) Number of new total and active FM puncta per bead. ***, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney test). (G) Accumulation of K48 polyUb (red) signal on presynaptic clusters by axonal proteasome and deubiquitinases inhibition. (H) Quantification of G (percentage of control). Four independent experiments. (I) Representative immunoblot of synaptosomal K48 Ub chains shows up-regulation at early postnatal development. Tubulin, loading control. (J) Axonal accumulation of K48 polyUb conjugates on beads (dashed circles; 4–5 h on the axonal side). Solid circles indicate off-bead. (K) K48 Ub intensity (normalized to off-bead). ***, P < 0.001 (Wilcoxon paired t test). (B, C, D, and H) ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; and *, P < 0.05 compared with control and ###, P < 0.001; ##, P < 0.01; and #, P < 0.05 (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Dunn´s multiple comparison test). n, microscope FOVs. (F and K) n, beads. Three independent experiments. Results are presented as mean values ± SEM. Bars, 5 µm.