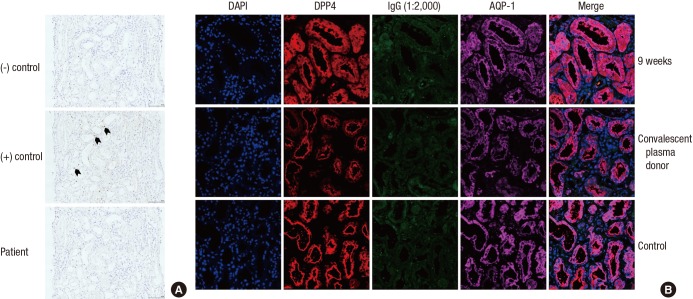
Fig. 3.
The detection of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus: in situ hybridization and confocal microscopy. (A) Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) was not evident in the in-situ hybridization method (magnification ☓ 200). The first and the second rows indicate negative and positive control (black arrow). The third row shows results from patients. There was no brown punctuate dot in the nucleus and/or cytoplasm. (B) The kidney tissue samples were co-stained for MERS-CoV (human IgG; green) and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP 4; red). DPP 4 was primarily stained in proximal tubules (aquaporin-1; violet). The first and second rows indicate the reaction using patient serum 9 weeks after symptom onset and the serum from a convalescent plasma donor. The third row is the negative control.