FIG 4 .
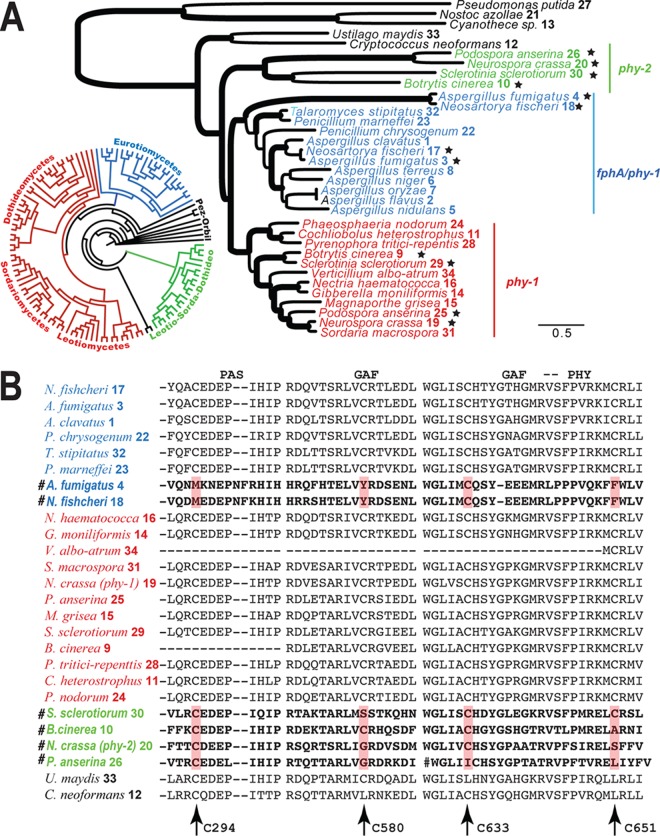
Evolution of phytochromes in fungi. Homologs were color coded for phy-1 (red), phy-2 (green), and fphA (blue), and sequences were numbered as in Table S2B in the supplemental material. (A) Maximum likelihood phylogeny of fungal phytochromes. Branches with strong support (BP of >85% or BPP of >0.98) are in boldface. Species with multiple copies of phytochromes are marked with stars. A circular tree shows a distribution of phytochromes in major ascomycetous groups. (Phylogenetic details are provided in Fig. S6 in the supplemental material.) (B) Excerpts of amino acid alignments of the PAS, GAF, and PHY domains. The cysteine sites putatively functioning in chromophore binding are indicated by arrows. PHY-1 of N. crassa was used as a reference for positions of the cysteine sites. Fast-evolving phytochromes are marked with the symbol #.