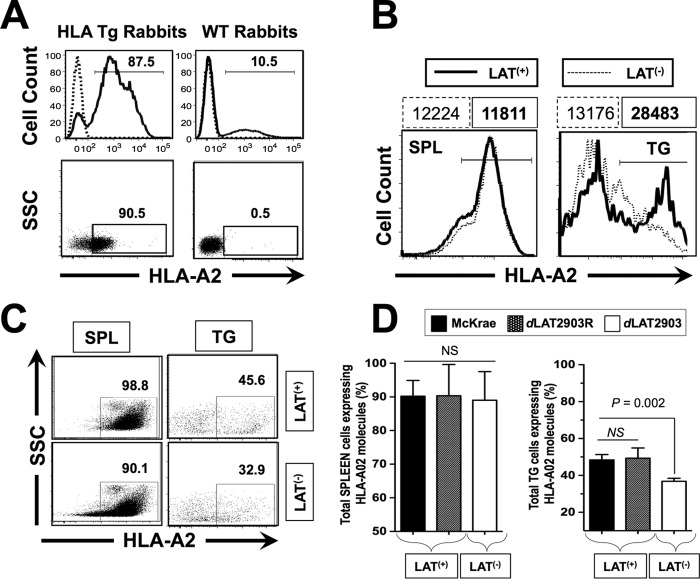
FIG 1.
HLA Tg rabbits infected with LAT+ virus have increased spontaneous virus shedding in tears and express high levels of HLA-A2 molecules in TG compared to HLA Tg rabbits infected with LAT– virus. (A) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from either HLA transgenic rabbits (HLA Tg rabbits) or from wild-type nontransgenic rabbit controls (WT rabbits) were stained with PE-conjugated anti-HLA-A2 MAb (clone BB7.2) and analyzed by flow cytometry for the relative expression of HLA-A2 molecules (top two panels) and for the percentage of cells expressing HLA-A2 molecules (bottom two panels). Rabbits with the highest levels of HLA-A2 molecules and with the highest percentages of cells expressing HLA-A2 molecules were selected for the remainder of the study. (B) LAT+ TG have increased levels of HLA-A2 molecules compared to LAT– TG. TG and spleens (control) from HLA Tg rabbits infected with either LAT+ or LAT– virus were removed on day 35 postocular infection. (C) Representative data of the percentages of total TG-derived cells expressing HLA-A2 molecules detected by FACS were compared in LAT+ TG versus LAT– TG. (D) Each bar represents the means ± the SD of the fluorescence intensity from two independent experiments from the spleen (control) and from TG harvested from five HLA Tg rabbits at 35 days postinfection. *, P < 0.05 (ANOVA).