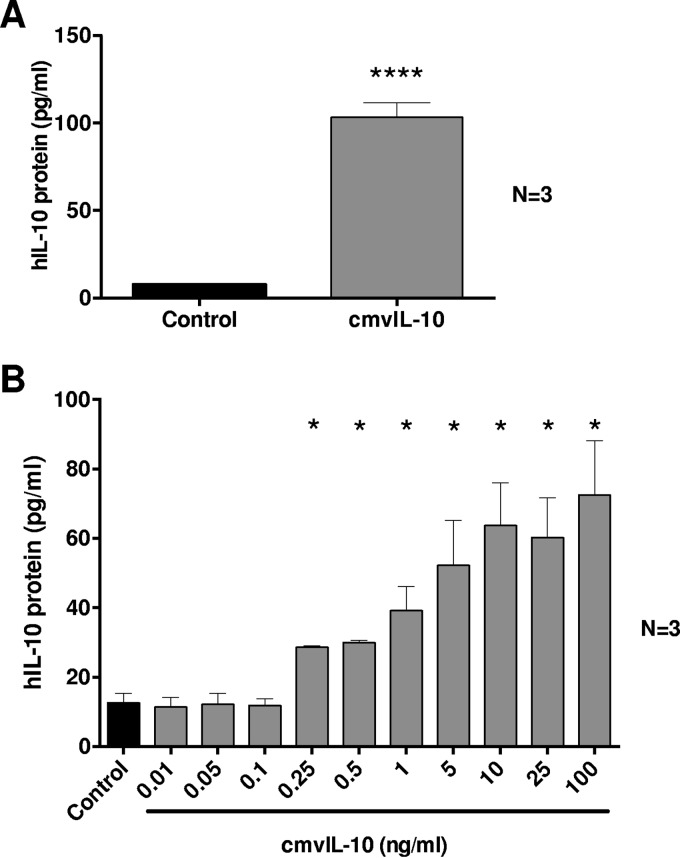
FIG 1.
Human CD14+ monocytes exhibit increased hIL-10 protein secretion in response to cmvIL-10. (A) ELISA-based quantitation of hIL-10 in the supernatants of cultures of primary human peripheral blood-derived CD14+ monocytes treated for 24 h with cmvIL-10 (100 ng/ml) or with phosphate-buffered saline (control). (B) Dose-dependent upregulation of hIL-10 secretion by CD14+ monocytes cultured with increasing concentrations of cmvIL-10 or with phosphate-buffered saline (control). The number (N) of independent biological replicate experiments is shown. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. Significant differences between results for the test samples and those of the control were determined using a two-tailed, paired Student's t test and are denoted by asterisks (*, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001).