FIG 1.
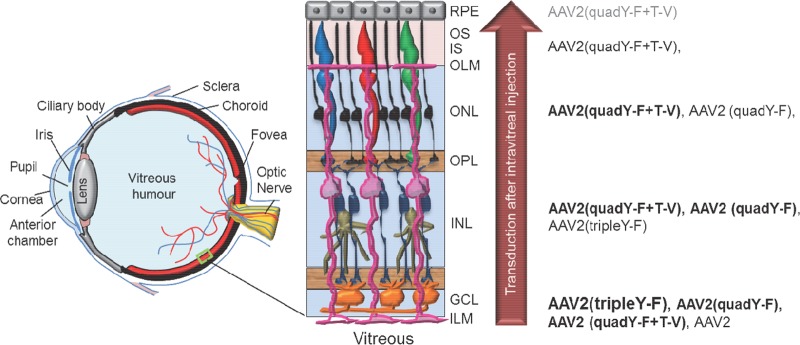
Schematic of the eye detailing the position of neural retina in the posterior segment, along with a higher-magnification view illustrating basic retinal anatomy. The inner limiting membrane (ILM) is a typical basement membrane at the vitreoretinal junction and is created by the end feet of Müller glia (pink). Müller glia span the entire width of the retina, forming barriers at each end, including the ILM in the inner retina and outer limiting membrane (OLM) in the outer retina. Between the ILM and OLM exist multiple nuclear and plexiform layers. The relative ability of previously described, AAV2-based vectors to transduce retinal neurons within these various layers following intravitreal injection is shown on the right. Strong transduction is depicted by large font/boldface letters, whereas weak transduction is depicted by smaller font/gray letters. While AAV2 transduces primarily ganglion cells within the inner retina, AAV2(quadY-F+T-V) promotes efficient transduction of middle retina, i.e., Müller cells (pink), bipolar cells (navy blue), horizontal cells (tan), and outer retina, i.e., photoreceptors (black/red/blue/green) and RPE (gray), following intravitreal delivery in mouse. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS, inner segments of photoreceptors; OS, outer segments of photoreceptors.