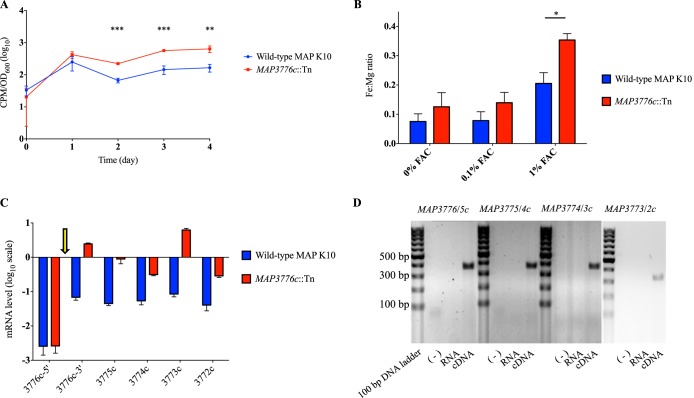
FIG 3.
Characterization of LSPP15. (A) 55FeCl3 uptake assay in wild-type M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis and MAP3776c::Tn. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (B) ICP-MS quantification of intracellular metal contents (Fe:Mg) of strains grown in the presence of 0%, 0.01%, and 1.0% FAC for 48 h. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations of the results of two individual experiments, each performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05 (compared with wild-type M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis intracellular Fe:Mg ratio). (C) Transcriptional analysis of LSPP15 genes in wild-type M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis and MAP3776c::Tn, quantified by qRT-PCR. Data shown are normalized to the expression of sigA, an endogenous housekeeping gene. The arrow indicates the transposon insertion. (D) Detection of cotranscription by amplifying the junction of each gene pair by PCR. Wild-type cDNA was used as a template; water and RNA served as negative controls. Lanes corresponding to reactions performed with each set of primers are separated by 100-bp DNA ladders (Thermo Scientific).