FIG 3.
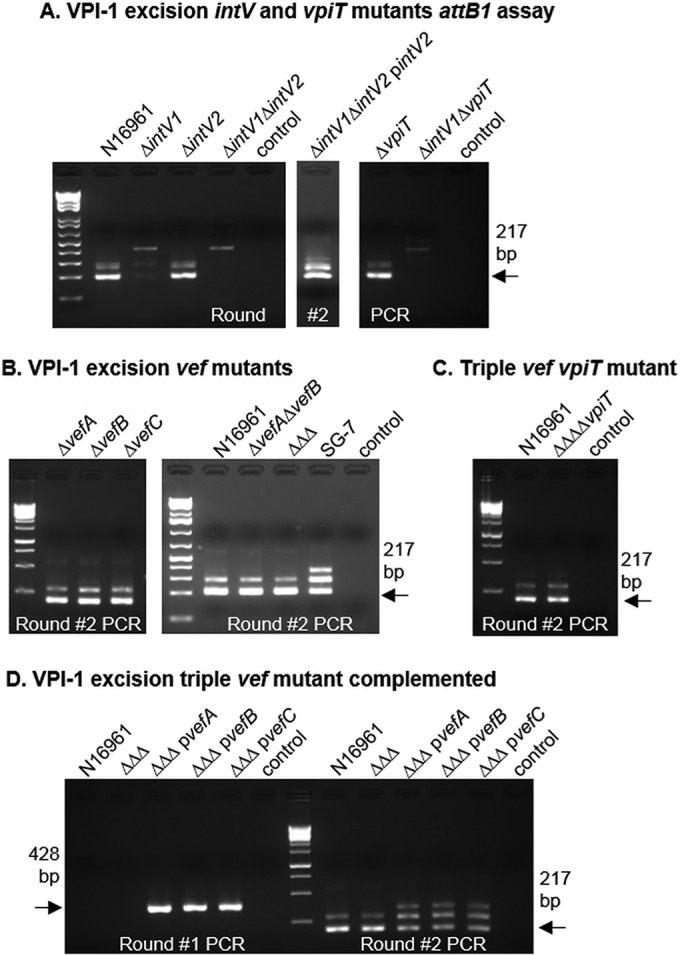
Role of integrases and RDFs in excision of VPI-1. (A) VPI-1 excision in the wild type (N16961) and intV and vpiT single and double mutants. The double intV mutant was complemented with intV2 to confirm the role of intV2 in VPI-1 excision. (B) Excision of VPI-1 using the attB1 excision assay in single, double, and triple (ΔΔΔ) RDF mutant backgrounds. (C) Excision of VPI-1 in the quadruple mutant (ΔΔΔΔvpiT), which lacks all three RDFs and the transposase encoded by vpiT. In panels A to C, the results of only round 2 are shown, as no excision products were detected in round 1. (D) VPI-1 excision in the ΔΔΔ mutant complemented with each RDF individually. Excision of the complements was detected in round 1 and is referred to as a superexcision phenotype. “control” indicates sample with no template DNA.
