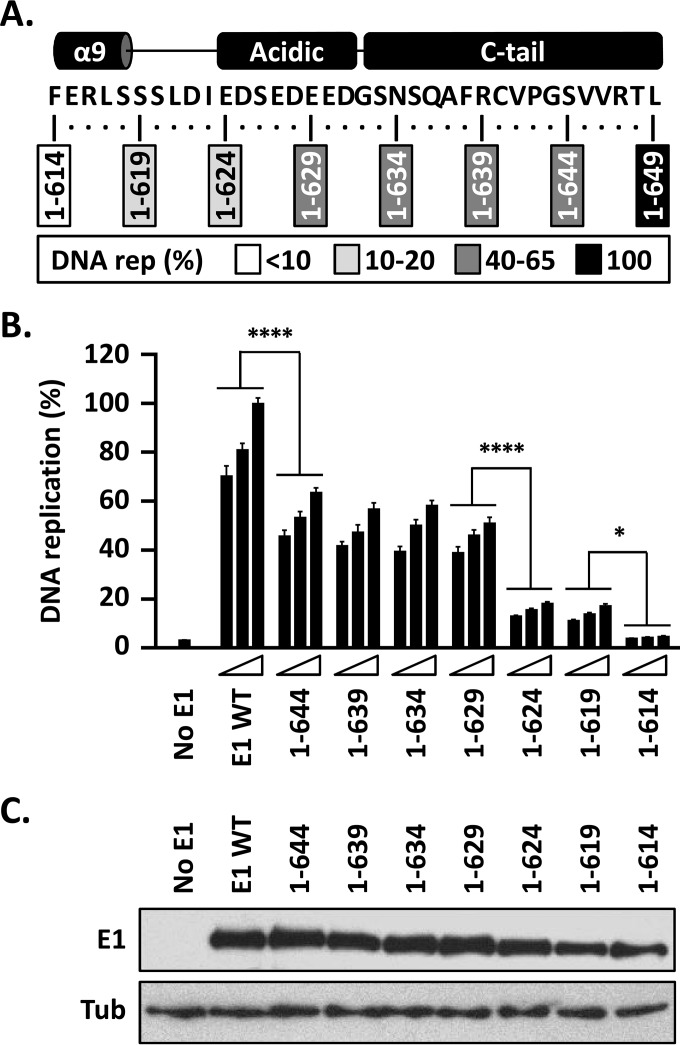
FIG 3.
The C terminus of E1 contains three subdomains that play roles in HPV11 DNA replication. (A) Schematic representation and amino acid sequence of the C terminus of HPV11 E1. The boxes indicate the amino acid residues retained in the C-terminally truncated E1 proteins; 1 to 649 refers to the wild-type protein. The boxes are shaded according to the levels of DNA replication (rep) supported by each E1 protein (as shown in panel B), with the darkest shade indicating the highest level of DNA replication and an open box indicating background levels of activity (<10%). (B) The DNA replication activities of the indicated E1 proteins were evaluated as described in the legend to Fig. 2, using three amounts of E1 expression vector (2.5, 5, and 10 ng). DNA replication levels were measured 72 h posttransfection and are reported as percentages of the levels obtained with 10 ng of wild-type E1 expression plasmid (WT). Statistical significance was assessed by comparing the DNA replication activity of each truncated E1 protein to that of the preceding (i.e., 5-amino-acid-longer) deletion using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc analysis. Significant differences are indicated (*, P ≤ 0.05; ****, P ≤ 0.0001). (C) Expression of GFP-tagged wild-type E1 and truncated derivatives. Extracts from transfected cells were separated on an SDS-10% PAGE gel prior to immunoblotting with an anti-GFP antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control.