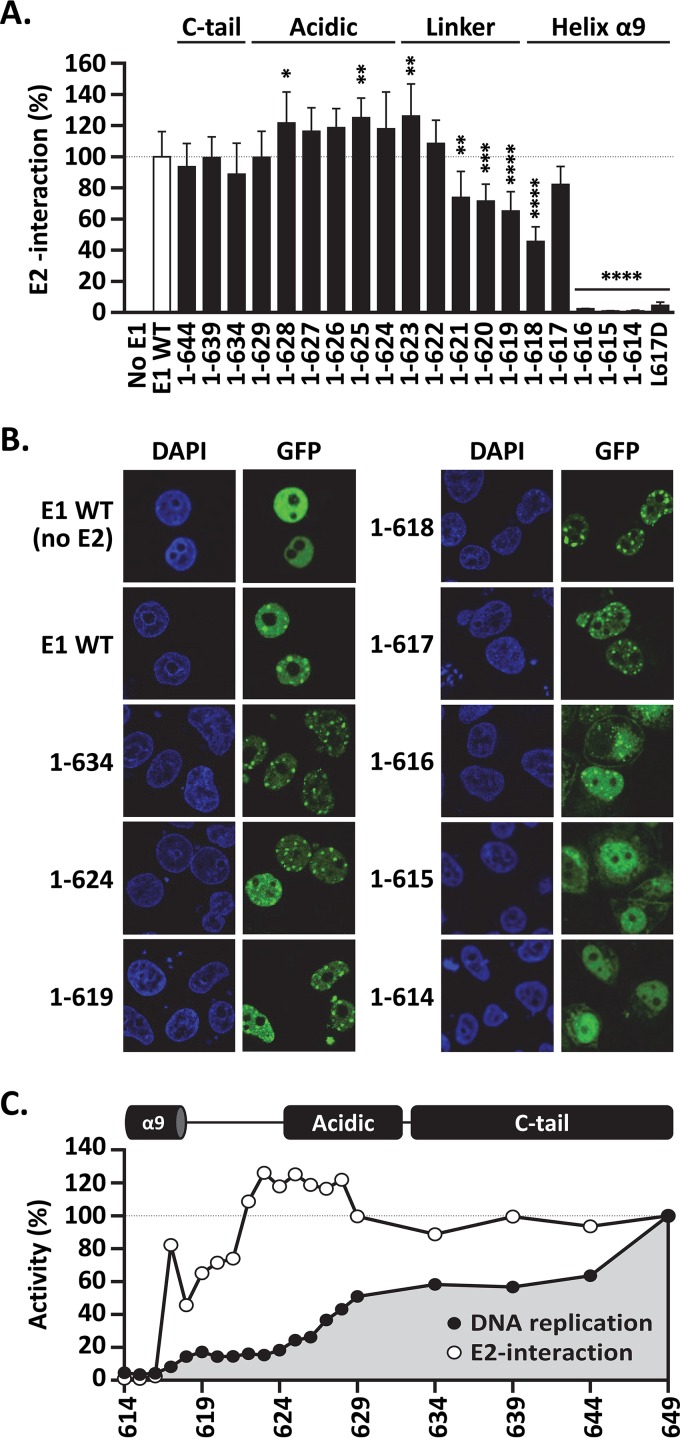
FIG 5.
C-terminal deletions that extend into helix 9 reduce interaction with E2. (A) LUMIER E1-E2 coimmunoprecipitation assay. Expression vectors for GFP-tagged wild-type E1 and truncated derivatives, as well as for the full-length L617D mutant protein, were cotransfected with a vector encoding E2 fused to Renilla luciferase (RLuc-E2). An empty vector encoding GFP alone (No E1) was used as a negative control. For each E1 protein, the amount of RLuc-E2 that was coprecipitated by GFP-E1 was determined by measuring the levels of Renilla luciferase activity and normalized to the amount of RLuc-E2 present in the input cellular extract. The amount of RLuc-E2 coprecipitated by wild-type GFP-E1 was set at 100%. Each bar represents the average of three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. Standard deviations are indicated by the error bars. Statistical significance was assessed by comparing the DNA replication activity of each E1 protein to that of wild-type GFP-E1 (white bar) using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc analysis. Significant differences are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). (B) Intracellular localization of the indicated GFP-E1 proteins in the presence of E2 (unless otherwise indicated). C33A cells transiently expressing the wild-type or truncated E1 proteins were visualized by fluorescence confocal microscopy. DNA was stained with DAPI to visualize the cell nuclei. Note the presence of GFP-E1 in E2-induced nuclear foci and the absence of such foci for E1(1–615) and E1(1–614). (C) Diagram summarizing the DNA replication and E2 interaction activities of the 19 truncated E1 proteins characterized in this study.