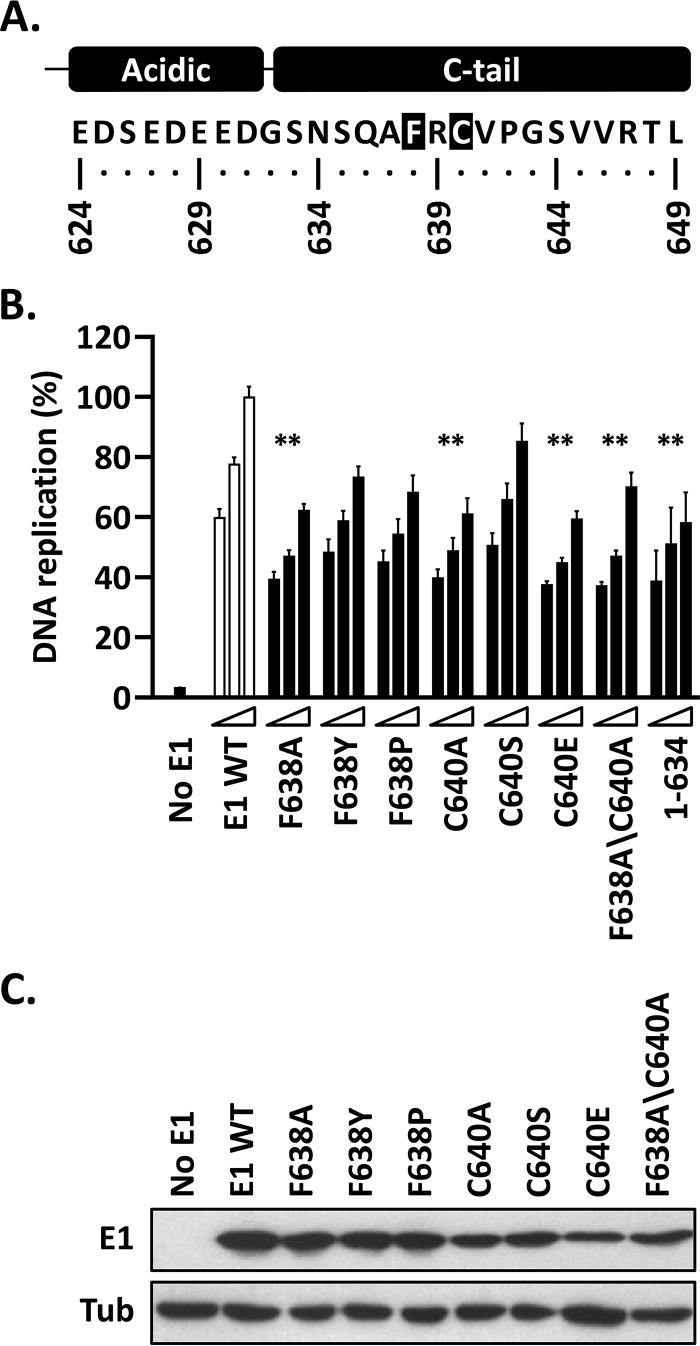
FIG 7.
Replacement of the highly conserved F638 and C640 residues in HPV11 E1 abrogates the function of the C-tail. (A) Representation and amino acid sequence of the C terminus of HPV11 E1 highlighting the two most highly conserved amino acid residues in the C-tail, F638 and C640. (B) Mutant E1 proteins carrying the indicated amino acid substitutions at F638 and/or C640 were evaluated for HPV11 DNA replication activity (as for Fig. 3B). The activity of E1(1–634), which lacks a functional C-tail, is shown for comparison. Statistical significance was assessed by comparing the DNA replication activity of each E1 protein to that of wild-type E1 (white bars) using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc analysis. Significant differences are indicated (**, P ≤ 0.01). (C) Expression of GFP-tagged wild-type E1 and mutant derivatives. Extracts from transfected cells were separated on an SDS-12% PAGE gel prior to immunoblotting with an anti-GFP antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control.