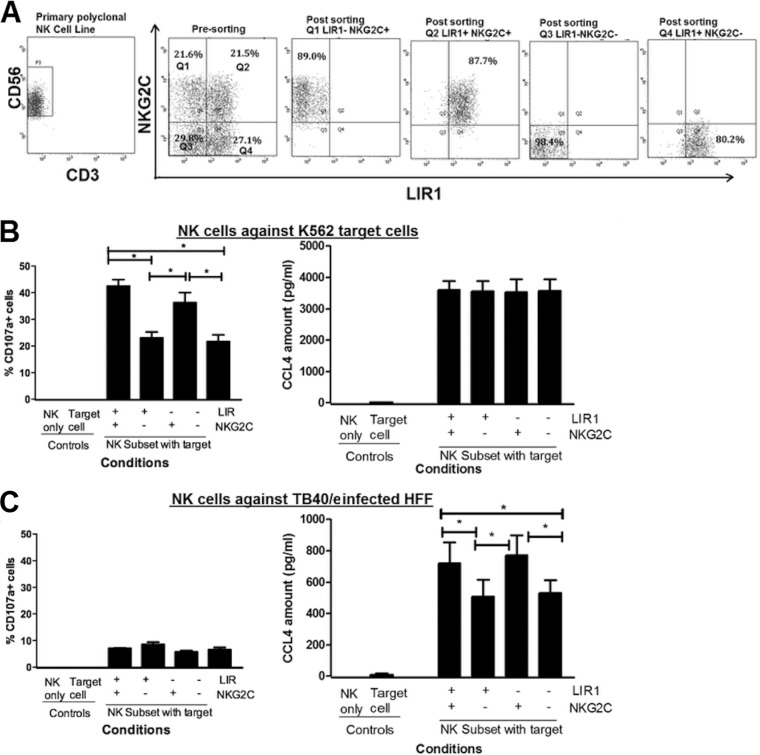
FIG 5.
The expression of NKG2C on in vitro-expanded NK cells has an effect on NK cell effector functions. (A) In vitro-expanded NK cells were stained with anti-CD3, -CD56, -LIR1, and -NKG2C antibodies and sorted by flow cytometry into four subsets based on LIR1 and NKG2C expressions. CD56+ CD3− NK cells were first collected (NK) before further sorting into LIR1− NKG2C+, LIR1+ NKG2C+, LIR1− NKG2C−, and LIR1+ NKG2C−. Representative dot plots of the NK cells before and after sorting are shown. Sorted NK cells were then cocultured with K562 targets (B) or HFFs infected with TB40/e at MOI of 5 (C). The NK cell-to-target ratio is 1:1. The percentages of CD107a+ cells were measured by flow cytometry after 5 h, and the levels of CCL4 cytokine secretion by NK cells were measured after overnight incubation. NK cell only and target cell only are the control samples. Error bars represent SEM. The experiment was repeated using 3 different donor NK cells (n = 3), and the average results were analyzed by the Student t test. Significant results (*, P < 0.05) are indicated.