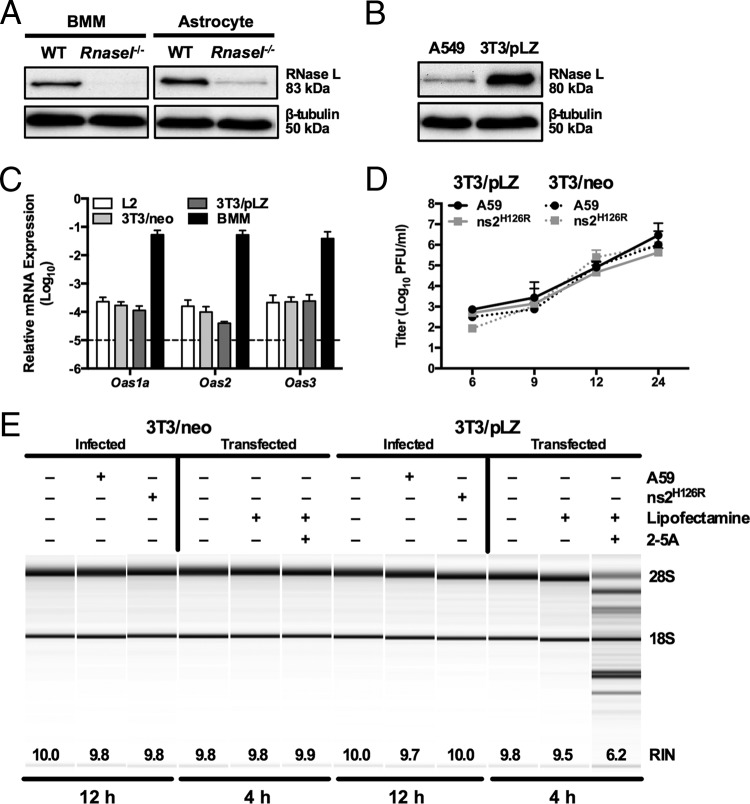
FIG 3.
Overexpression of RNase L is not sufficient to overcome low OAS levels to promote RNase L degradation. (A) Proteins were extracted from WT and Rnasel−/− BMM and astrocytes, electrophoresed in polyacrylamide gels, and probed by Western blotting with antibodies directed against RNase L (rabbit polyclonal) and β-tubulin. BMM and astrocyte lysates were electrophoresed on the same gel and blot; intervening lanes were removed and replaced by spaces between samples. (B) Proteins were extracted from human A549 and murine 3T3/pLZ cells, electrophoresed in polyacrylamide gels, and probed by Western blotting with antibodies directed against human RNase L and human β-tubulin. (C) RNA was extracted from L2, 3T3/pLZ, 3T3/neo, and BMM cultures, and basal expression levels of Oas mRNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR. mRNA expression levels relative to β-actin mRNA are expressed as 2−ΔCT, where ΔCT is equal to CT Target Gene minus CT β-actin. The data are from one representative experiment of two (except for pLZ/neo mRNA), each performed in triplicate. The dashed line indicates the lower limit of detection. The error bars indicate SEM. (D) 3T3/pLZ and 3T3/neo cells were infected with A59 or ns2H126R (1 PFU/cell), and at the times indicated, the virus titer was determined by plaque assay of the supernatant. The data are pooled from two independent experiments (3T3/pLZ) or from one experiment (3T3/neo), each performed in triplicate. (E) 3T3/pLZ and 3T3/neo cells were mock infected or infected with A59 or ns2H126R (1 PFU/cell), and at 12 h postinfection, the cells were lysed and RNA was extracted. In a separate experiment, cells were transfected with 10 μM 2-5A in Lipofectamine or with Lipofectamine alone or were left untreated, and 4 h later, the cells were lysed and RNA was extracted. rRNA degradation was assessed with a bioanalyzer. 28S and 18S rRNAs are indicated.