FIG 3.
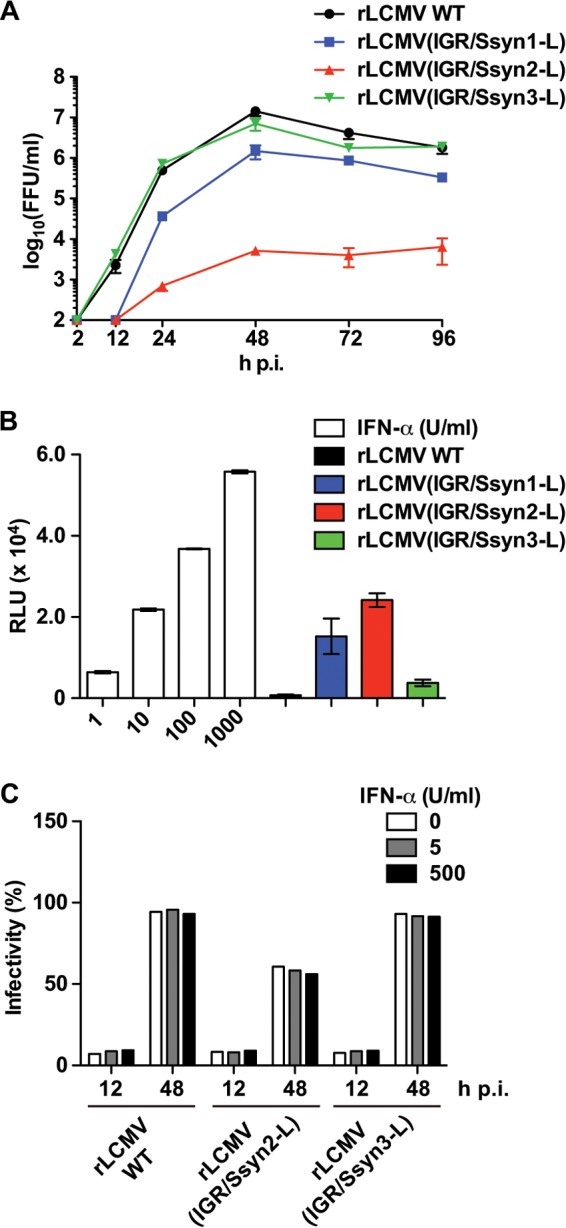
Growth of rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn-L) in IFN-competent cells. (A) Growth kinetics of the rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn-L) constructs in IFN-competent A549 cells. A549 cells were infected with the rLCMV WT or an rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn-L) construct (MOI = 0.01). Virus titers in the TCS were determined at the indicated times p.i. Data represent the means ± SDs from three independent experiments. (B) Ability of the rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn-L) constructs to induce ISRE-mediated reporter gene expression. A549/ISRE-Fluc cells were infected with the rLCMV WT or an rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn-L) construct (MOI = 0.1) or treated with IFN-α at the concentrations indicated on the x axis, and 17 h later, the levels of Fluc activity were determined. Values of Fluc activity from mock-infected and untreated cells were subtracted as background activity. Data represent the means ± SDs from three independent experiments. RLU, relative light units. (C) Sensitivity of rLCMVs to exogenous IFN-I. Vero cells were infected with the rLCMV WT, rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn2-L), or rLCMV(IGR/Ssyn3-L) (MOI = 0.05) for 90 min and treated with IFN-α (5 or 500 U/ml) or left untreated. At 12 and 48 h p.i., cells were fixed and virus infectivity was determined by IFA.
