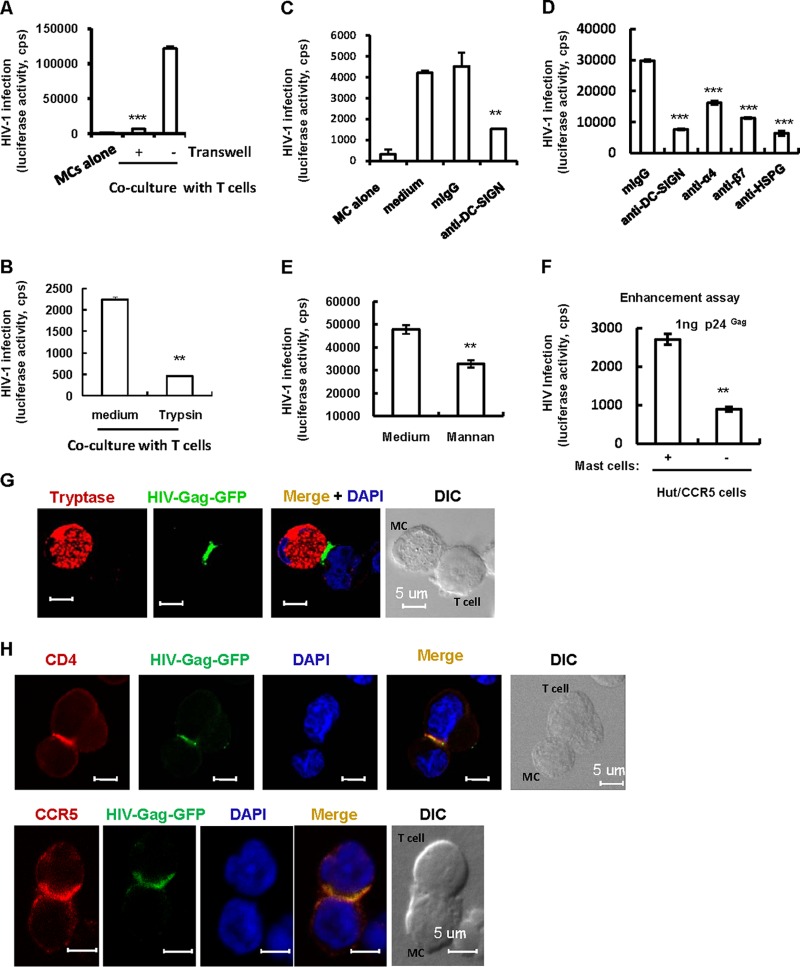
FIG 3.
Mucosal mast cells mediate HIV-1 trans-infection of CD4+ T cells. (A) Viral trans-infection. Freshly isolated mucosal mast cells were incubated with single-cycle infectious HIV-luc/JRFL for 2 h. Virus-harboring cells were washed and cocultured with or without CD4+ Hut/CCR5 T cells, and HIV trans-infection was determined after 2 days by measuring the luciferase activity. Where indicated, a transwell culture plate with a 0.4-μm insert membrane was used to separate the virus-loaded mast cells from the target cells. (B) Treatment with trypsin to remove surface-bound viral particles before coculture diminished viral trans-infection. (C to E) Pretreatment with antibodies against DC-SIGN, HSPG, or α4β7 integrin or with mannan prior to viral inoculation diminished mast cell-mediated transmission. (F) Enhancement assay. HIV-luc/JRFL-pulsed mast cells were cocultured with Hut/CCR5 cells, or the same amounts of cell-free viruses were added directly to T cells, and viral infection was measured as described above after 2 days of culture. (G) Visualization of the cell-cell conjunction between mucosal mast cells and T cells by confocal microscopy. After 2 h of exposure to HIV-Gag-GFP/JFRL, mast cells were washed and cocultured with Hut/CCR5 cells for 1 h. Cells were fixed and immunostained for intracellular tryptase (red); nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (H) Recruitment of viruses, CD4, and CCR5 to conjunction sites. Data in graphs are means and standard deviations (SD). Results are representative of three independent experiments. cps, counts per second. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (paired t test).