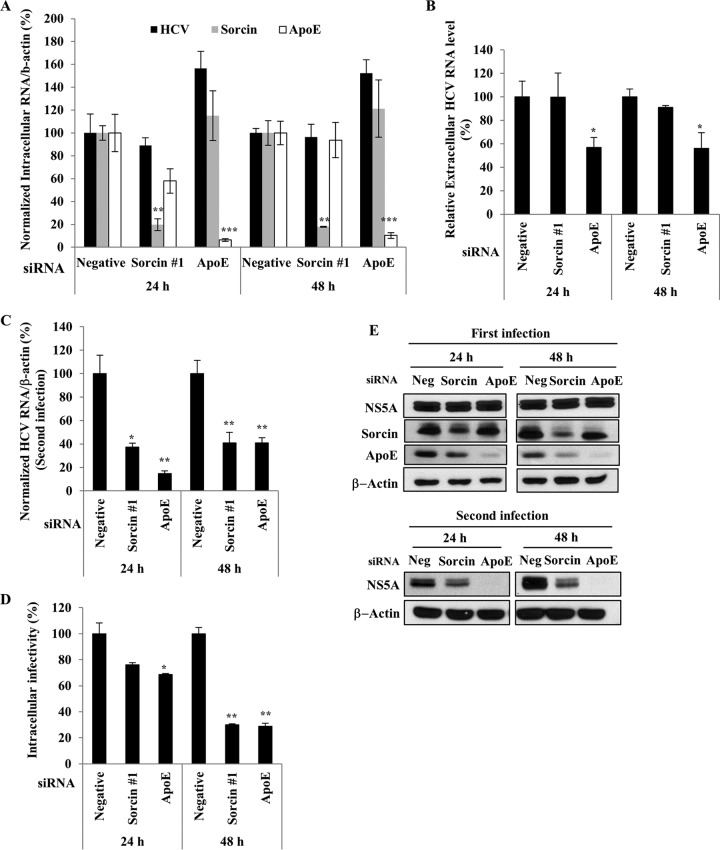
FIG 6.
Sorcin is required for a late step of the HCV life cycle. (A and B) Huh7.5 cells were infected with Jc1 for 4 h. At 48 h postinfection, cells were transfected with a 20 nM concentration of the indicated siRNAs. At 24 h after siRNA transfection, medium was replaced with fresh DMEM containing antibiotics. At the indicated time points, intracellular RNA levels (A) and extracellular HCV RNA levels (B) were determined by qRT-PCR. (C) Naive Huh7.5 cells were infected with Jc1 harvested from culture supernatants of the experiment shown in panel A, and viral infectivity was determined by measuring intracellular HCV RNA levels by qRT-PCR. (D) Huh7.5 cells treated as described in panel A were lysed with three cycles of freezing and thawing and centrifuged at 15,000 × g for 15 min in a 4°C microcentrifuge. The supernatant was collected to determine intracellular HCV infectivity. Naive Huh7.5 cells were infected with Jc1 harvested from the intracellular supernatant for 4 h. At 48 h postinfection, relative intracellular HCV infectivity was determined by qRT-PCR. (E) Huh7.5 cells were infected with Jc1 for 4 h (upper panel). At 48 h postinfection, cells were transfected with a 20 nM concentration of the indicated siRNAs. At the indicated time points, protein levels were determined by immunoblot assays using the indicated antibodies. For the second infection (lower panel), naive Huh7.5 cells were infected with Jc1 harvested from culture supernatants of the experiment described for the upper panel. At 48 h postinfection, protein levels were determined by immunoblot assays using the indicated antibodies. Negative (or Neg), universal negative-control siRNA.