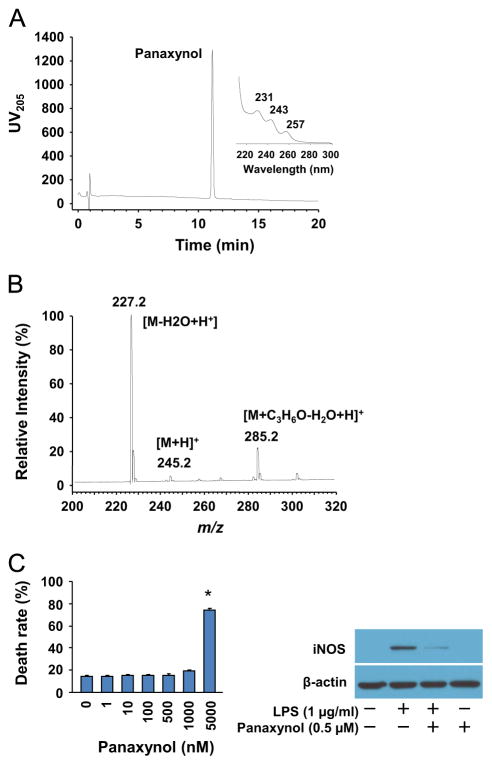
Fig. 2.
Isolation of panaxynol from hexane fraction of American ginseng. (A) LC–UV DAD analysis of purified panaxynol from hexane fraction of American ginseng. (B) LC–MS analysis of purified panaxynol from hexane fraction of American ginseng. (C) Left panel: Cytotoxicity of panaxynol in RAW264.7 cells. Sub-confluent RAW264.7 cells were treated with or without panaxynol in DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS as indicated for 24 h. n=6, *p<0.05 vs. control (0). Right panel: The effect of panaxynol on iNOS expression in LPS-inflamed RAW24.7 cells. Sub-confluent RAW264.7 cells were treated with LPS and panaxynol in DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS as indicated for 6 h. The immunoblotting results are representative of three separate experiments.