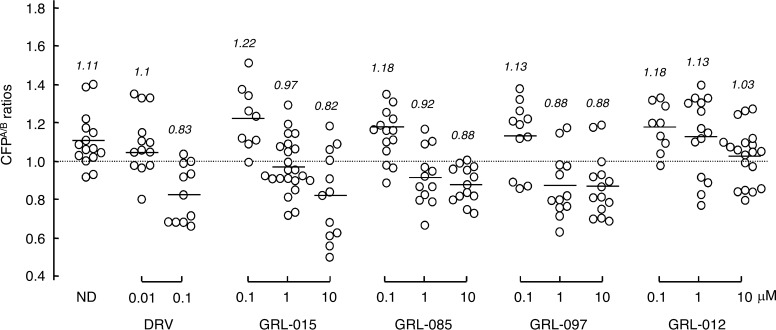
FIG 4.
Inhibition of HIV-1 protease dimerization. COS7 cells were exposed to each of the agents (GRL-015, -085, -097, and -012 and DRV) at various concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 μM) and subsequently cotransfected with plasmids encoding full-length molecular infectious HIV-1 (HIVNL4-3) clones, producing CFP- or YFP-tagged protease. After 72 h, cultured cells were examined in the FRET-based HIV-1 expression assay, and the CFPA/B ratios (y axis) were determined. The mean values of the ratios obtained are shown as horizontal bars. A CFPA/B ratio greater than 1 signifies that protease dimerization occurred, whereas a ratio less than 1 signifies the disruption of protease dimerization. All the experiments were conducted in a blinded fashion. Statistical differences were as follows: for the CFPA/B ratios in the absence of drug (CFPA/BNo Drug) versus the CFPA/B ratios in the presence of 0.01 μM DRV (CFPA/B0.01 DRV), P = 0.5846; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B0.1 DRV, P = 0.0002; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B0.1 GRL-015, P = 0.1784; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B1 GRL-015, P = 0.0021; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B0.1 GRL-085, P = 0.2006; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B1 GRL-085, P = 0.0033; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B0.1 GRL-097, P = 0.4482; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B1 GRL-097, P = 0.0006; for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B1 GRL-012, P = 0.1189; and for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B10 GRL-012, P = 0.0007.